- No products in the cart.
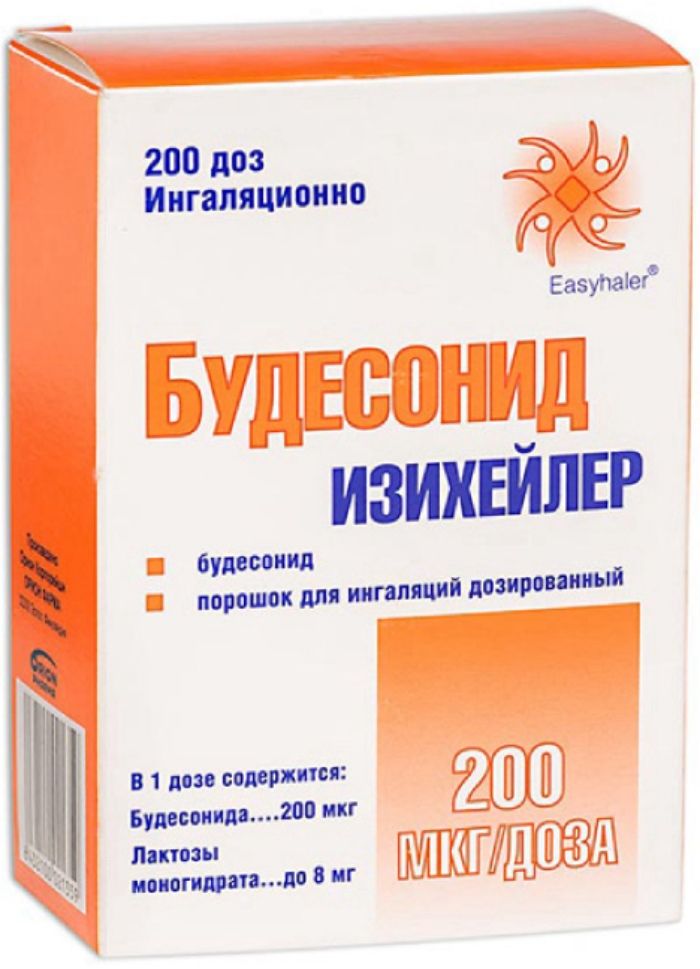
Budesonide iziheyler powder ing.dozir. 200mkg / dose inhaler 200doz

Solgar lozenges 50 pcs Flavio zinc
$14.54
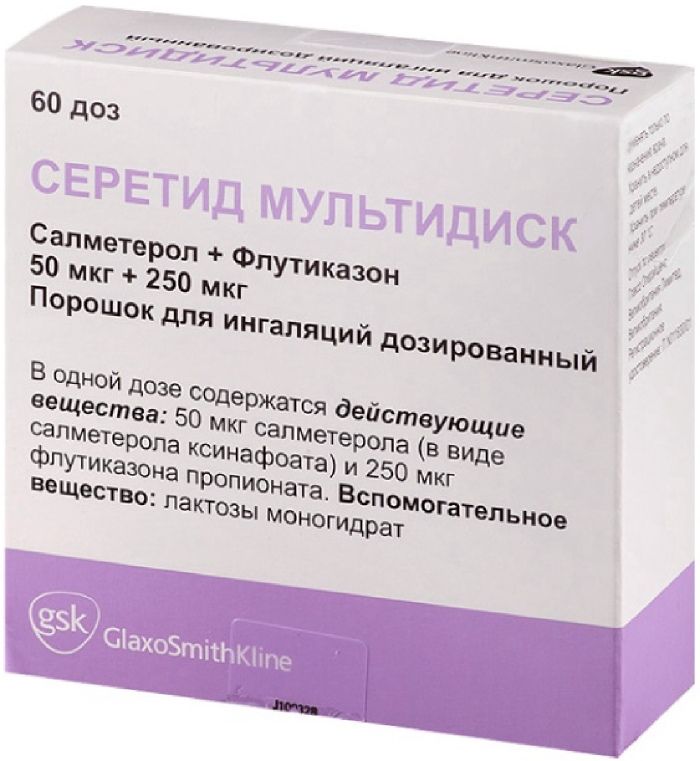
Seretide multidisk powder ing.dozir. 50mkg / 250mkg 60doz with inhaler
$33.31
$28.66
Budesonide iziheyler powder ing.dozir. 200mkg / dose inhaler 200doz
Description
Composition
Active substance:
budesonide – 0.2 mg
Excipients:
lactose monohydrate – 7.8 mg
Description:
The inhaler of the polymeric material. On the part of the dispensing device is fitted with locking cap. The front part of the device applied to the inscription «Easyhaler®». Side counter is the number of remaining doses. Content inhaler – a homogeneous powder of white or nearly white, without indecomposable agglomerates.
Product form:
Powder for inhalation dose, 200 mg / dose.
2.5 g product (200 doses) is placed in the inhaler from a polymeric material. Each inhaler is packaged in a foil pouch with aluminum laminated. 1 the inhaler, sealed in a foil pouch of laminated aluminum, together with instructions for use placed in a pile of cardboard.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to budesonide, children under 6 years as well as rare inherited disease, such as lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption (since the drug contains lactose).
Precautions: tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial and viral infections, respiratory, hepatic cirrhosis, glaucoma, hypothyroidism, osteoporosis, pregnancy, breast-feeding.
Indications
Bronchial asthma, mild, moderate and severe, treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Interaction with other drugs
The metabolic conversion of budesonide is carried out mainly at the participation of isoenzyme CYP3A4. Simultaneous reception isoenzyme CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, cyclosporine, ethinylestradiol and troleandomycin) may lead to a multiple increase in the concentration of budesonide in the plasma. For short course therapy (1-2 weeks), this increase is of little clinical significance, but with a long reception it should be taken into account. Since there is no data to provide the desired dosage in such cases, the combinations of these drugs with budesonide should be avoided. If you avoid the combination of these drugs is not possible, to maximize the amount of time between the reception of these drugs and consider reducing the dose of budesonide. A few details regarding this interaction for high doses of inhaled budesonide indicate the possibility pronounced increase its level in plasma (average of 4-fold), while the use of inhaled budesonide once (in a dose of 1000 ug) with itraconazole at a dose of 200 mg once a day. Methandrostenolone, estrogens increase the effect of budesonide.
Increasing concentrations of glucocorticoids in the blood plasma and increased their activities was observed in women who are at the same time with glucocorticosteroids administered estrogen and steroidal contraceptives, but no effect was observed in the budesonide therapy and concomitant reception of low-dose combined oral contraceptive pill.
In view of the possibility of adrenal suppression, ACTH stimulation test for the diagnosis of pituitary insufficiency may give false results (low values).
Overdose
symptoms of overdose
Frequency acute toxic reactions to budesonide is low. Prolonged use of excessive doses can develop systemic reactions on steroids, such as increased sensitivity to infection and the development of Cushing adrenal suppression. There may be atrophy of the adrenal cortex and impaired ability to adapt to stress.
Drug therapy with the drug overdose
In acute overdose specific emergency treatment is required. Treatment with inhaled budesonide should be continued in the dose recommended for the control of bronchial asthma. The “hypothalamus – pituitary – adrenal cortex” is restored in a few days. In stressful situations, it may be necessary as a precautionary measure to appoint corticosteroids (eg, high-dose hydrocortisone) systemically. Patients with atrophy of adrenal steroid find and to achieve stabilization pick them adequate maintenance therapy with systemic corticosteroids.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
glucocorticosteroid for topical application.
Pharmacodynamics:
Budesonide is a glucocorticosteroid with a strong local anti-inflammatory action. Improved control of bronchial asthma after the inhalation of budesonide can develop within 24 hours after the beginning of therapy, while the maximum effect is achieved after several weeks of continuous use of the drug. Mechanisms of action of corticosteroids on inflammation in asthma is not exactly known. The anti-inflammatory action such as suppression of the release of mediators of inflammation or cytokine-mediated immune response, perhaps the most important. Budesonide reduces airway reactivity in response to inhaled histamine and methacholine. Therapy inhaled budesonide is effective for the prevention of bronchial asthma physical stress. Shown a dose-dependent effect on the cortisol content in plasma and urine in patients receiving budesonide. At recommended dosages budesonide has a less pronounced effect on the adrenal function than prednisolone at a dose of 10 mg, as was shown in ACTH tests. In long-term studies in clinical practice it has shown that most children and adolescents treated with inhaled budesonide ultimately achieve the necessary growth for adults. However, there was an initial slight temporary stunting (approximately 1 cm), usually within the first year of treatment. It was also shown that the use of inhaled budesonide in children (5-16 years old) with bronchial asthma, budesonide received an average daily dose of 504 micrograms for 3-6 years old, was not associated with increased incidence of posterior subcapsular cataract.
Pharmacokinetics:
Budesonide – active substance of the preparation – is a mixture of two isomers (22R and 22S). The glucocorticosteroid receptor affinity studies indicated that the 22R isomer is 2-fold more potent than isomer 22S. These two formulations of budesonide are not exposed interconversion. Period for the final half-life is the same for both isomers (2 – 3 hours). In patients with asthma about 15-25% of the inhaled dose as part of the drug budesonide reaches the bronchial tubes. The most significant part of the inhaled dose remains in the oropharynx is swallowed and (if not rinse the mouth).
Suction
After assigning budesonide inwardly maximum drug concentration achieved in about 1-2 hours in plasma and the absolute systemic bioavailability of 6-13%. In plasma, 85-95% budesonide associated with the protein. Maximum plasma concentration is achieved approximately 30 minutes after inhalation. The bulk of the budesonide to the lungs, is absorbed into the systemic circulation.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of budesonide is about 3 l / kg. Plasma protein binding is on average 85-90%.
Metabolism
Budesonide rapidly and largely metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P4503A4 system with formation of two major metabolites. Glucocorticosteroid in vitro activity of these metabolites is less than 1% of the activity of the starting material. In small quantities, it is metabolized in the lungs and blood serum.
allocation
Budesonide is excreted in the urine and feces in the form of conjugated and unconjugated metabolites.
Linearity
Kinetics proportional to the dose of budesonide in clinically relevant dose range.
Separate groups of patients
In patients with liver diseases degree of bioavailability of budesonide may increase.
In children aged 4-6 years old, suffering from bronchial asthma, systemic clearance of budesonide is about 0.5 l / min. In terms of per kilogram of body weight clearance of budesonide in children by about 50% higher than that of adults. In children suffering from bronchial asthma, terminal half-life of budesonide is about 2.3 hours. This figure almost matches that of the adults.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Pregnancy Most of the results from prospective epidemiological studies and post-marketing use of world experience suggests that treatment with budesonide during pregnancy has not been accompanied by an increased risk of adverse effects in the fetus or newborn. Continuation of adequate treatment of asthma during pregnancy is important for both the mother and the fetus. Appointment of budesonide inhalation during pregnancy should only be undertaken in cases where the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Should apply the minimum dose of budesonide needed to ensure an adequate asthma control.
Breast-feeding
Budesonide is excreted in breast milk. However, in therapeutic doses, as expected, it has no impact on infants who are breastfed. Permitted use of inhaled budesonide during breast-feeding a baby.
Supportive therapy nursing mothers inhaled budesonide (200 or 400 mcg twice daily) results in negligible systemic exposure of budesonide to suckling.
The calculated pharmacokinetic study the daily dose of budesonide is in the child was 0.3% of the daily dose for both maternal dose levels, and the average concentration of budesonide in the blood plasma of children was 1/600 part by the drug concentration in the blood plasma of mothers, taking into full attention to bioavailability of the drug when administered in infants. The concentration of budesonide in all blood plasma samples of children was below the limit of quantitation.
Based on the data obtained in the study of budesonide inhalation, as well as the linear pharmacokinetics of budesonide in the therapeutic range after intranasal, inhalation, oral or rectal administration, it is expected that when using the drug at therapeutic doses its effect on the infant will be low.
Prescribe inhaled budesonide nursing mothers should be only in cases where the expected positive effect on a woman’s body is greater than any possible risk to the child.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Prescription.
side effects
Possible adverse effects presented by organ systems and distributed development rate.
Very frequent (> 1/10)
Frequent (> 1 / 100-
special instructions
Inhaler Budesonide Iziheyler not intended for the treatment of established acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. These conditions should be treated in accordance with the guidelines and use of short-acting bronchodilators. Patients should remember that the inhalation powder budesonide Iziheyler a prophylactic drug, and therefore to ensure optimum effect it must be used regularly, even in the absence of asthma symptoms, and do not stop taking abruptly. Translation patients receiving glucocorticoids inside to inhaled glucocorticosteroids, and further treatment require additional therapeutic measures. Prior to initiation of therapy a high dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroids, taken twice a day, for a bronchial asthma patient must be stable enough and inhalation should be performed in addition to the usual maintenance dose systemic glucocorticosteroids. Approximately 10 days later start cancellation systemic glucocorticosteroids, gradually reducing their daily dose (e.g., monthly, reducing the dose to 2.5 mg of prednisolone or another drug – the equivalent value) to the minimum possible level. Sometimes it can be a complete replacement of receiving glucocorticoids inside for inhalation. Patients who requested emergency treatment with high doses of corticosteroids or long-term treatment with the use of the highest recommended dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroids may impair the function of the adrenal glands. In these patients in a severe stress may appear symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. In times of stress or exposure during scheduled surgical interventions should consider the need for additional systemic corticosteroids destination. In patients previously treated with oral corticosteroids for a long time, perhaps the appearance of symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. Restoring adrenal function after discontinuation of oral corticosteroids may take a long time, and therefore in patients receiving long-term oral steroids and transferred to inhaled budesonide may be stored for a long time the risk of adrenal insufficiency symptoms. In such cases, a regular function of the system control “of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex”. When translated from the receiving glucocorticosteroid budesonide inwards on inhalation may develop symptoms which previously suppressed systemic glucocorticoid therapy, e.g., the symptoms of allergic rhinitis, eczema, muscle and joint pains. For relief of symptoms to treatment should be added to these specific treatments. Some patients may develop a general malaise caused by the abolition of systemic administration of corticosteroids, despite the preservation or even improvement in respiratory function. In such cases, patients should be configured to continue the treatment with inhaled budesonide and the abolition of glucocorticosteroids inside, except the appearance of clinical indications for the abolition of inhalation, for example, symptoms indicating the presence of adrenal insufficiency. As with other methods of inhalation therapy, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur, manifesting gain immediate wheezing and the feeling of lack of air inhaled after the dose. Paradoxical bronchospasm cropped quick inhaled bronchodilators, and treatment should be carried out immediately. You should immediately cancel the budesonide conduct examination of the patient and, if necessary, appoint alternative therapies.
If, in spite of appropriate control treatment, there was an episode of acute dyspnea, it is necessary to apply the fast acting inhaled bronchodilator and revise the prescribed treatment. In cases where, in spite of the maximum dose of inhaled corticosteroids asthma symptoms fail to properly monitor, patients may require short course of systemic corticosteroids. In such situations, should therapy with inhaled corticosteroids supplemented with systemic drugs. Systemic effects of inhaled glucocorticosteroids reception may occur, particularly at high doses for a long period of time. These effects are much less likely than the consequences of receiving oral glucocorticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include Cushing’s syndrome, Kushingoid appearance, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decrease in bone mineral density, cataract, glaucoma and, much less, a variety of psychological and behavioral problems, including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression or aggression (particularly in children). It is therefore very important that the dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroid was brought to a minimum level that maintains the effectiveness of asthma control.
May increase the risk of pneumonia in patients with newly diagnosed COPD starting treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids. In children receiving prolonged treatment with inhaled corticosteroids it is recommended to regularly measure growth. If growth slows, should review the treatment regimen to reduce the dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroid, if possible, to the minimum, to retain effective control of bronchial asthma. In addition, you must refer the patient to a pediatric pulmonologist. During therapy with inhaled glucocorticosteroids can be observed oral mucosal candidiasis. To reduce the risk of mucous oral candidiasis and hoarseness patients have good mouth rinse or brush after every Hour inhaled glucocorticosteroid. Candidiasis may require treatment with appropriate antifungal drugs, and some patients may even be necessary to discontinue treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids. Exacerbation of clinical manifestations of asthma may be due to acute bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, and thus may require treatment with appropriate antibiotics. In such cases, patients sometimes have to increase the dose of inhaled budesonide and conduct a short course of corticosteroids therapy inside. As an emergency treatment for relief of asthma attacks to be applied fast inhaled bronchodilators. Перед началом терапии ингалятором Будесонид Изихейлер у пациентов с активной или неактивной формой туберкулеза легких необходимо провести специфические диагностические и адекватные специфические лечебные мероприятия для обеспечения контроля этого заболевания.
Аналогично у пациентов с грибковыми, вирусными или другими инфекциями дыхательных путей необходимо обеспечить тщательное наблюдение и специфическую терапию и использовать ингалятор Будесонид Изихейлер только в случаях, когда обеспечена адекватная терапия этих инфекций. У пациентов с избыточной секрецией слизи в дыхательных путях может потребоваться короткий курс терапии глюкокортикостероидами внутрь. У пациентов с нарушениями функции печени лечение ингаляциями будесонида может приводить к снижению скорости выведения глюкокортикостероидов, и, следовательно, к повышению их системной биодоступности. При этом могут развиваться системные эффекты препарата, поэтому у таких пациентов следует регулярно контролировать функцию системы «гипоталамус – гипофиз – кора надпочечников». Следует избегать одновременного приема кетоконазола и других мощных ингибиторов изофермента CYP3A4. Если это невозможно, интервалы времени между приемами взаимодействующих препаратов следует устанавливать максимально большими. Пациентам с редкими наследственными синдромами непереносимости галактозы, недостаточности лактазы (синдром Lapp) или глюкозо-галактозной мальабсорбцией этот препарат принимать нельзя. Лактоза – вспомогательное вещество, входящее в состав данного лекарственного препарата – содержит небольшие количества молочных белков, и поэтому может вызывать аллергические реакции.
Effect on the ability to drive mechanisms and
In connection with the development of neuropsychiatric symptoms should observe caution when driving vehicles and mechanisms.
Storage conditions
Хранить при температуре не выше 30 градусов, в недоступном для детей месте.
После вскрытия алюминиевого пакета использовать в течение 6 месяцев.
Dosing and Administration
Inhalation.
Для обеспечения оптимального ответа на лечение препарат Будесонид Изихейлер следует принимать регулярно. При переводе пациентов на терапию ингалятором Будесонид Изихейлер с других ингаляторов схему лечения следует подбирать индивидуально. При этом необходимо учитывать особенности ранее применявшихся препаратов, схемы лечения, способ применения лекарственного вещества. Пациентам следует назначать начальную дозу ингалируемого будесонида, соответствующую степени тяжести или уровню контроля течения заболевания.
Терапевтический эффект наступает через несколько дней после начала приёма препарата и достигает своего максимума через несколько недель лечения. Дозу препарата необходимо регулировать до достижения полного контроля над заболеванием, а после этого начать её постепенное снижение до минимальной дозы, обеспечивающей сохранение эффективного контроля над астмой.
Начальная доза у взрослых (включая пожилых и детей/подростков старше 12 лет) при бронхиальной астме легкого течения (ступень 2) и у детей 6–12 лет составляет 200–400 мкг/сутки. При необходимости дозу можно увеличить до 800 мкг/сутки. У взрослых пациентов с бронхиальной астмой среднетяжелого (ступень 3) и тяжелого (ступень 4) течения начальная доза может составлять до 1600 мкг/сутки. Поддерживающую дозу следует подбирать в соответствии с тяжестью заболевания и клиническим ответом. Дозу следует корректировать до достижения контроля течения заболевания, после чего постепенно уменьшать до минимальной, при которой эффективный контроль течения заболевания еще сохраняется.
Дозирование два раза в сутки Взрослым пациентам с бронхиальной астмой легкого, среднетяжелого и тяжелого течения (включая пожилых и детей/подростков старше 12 лет): обычно поддерживающая доза составляет 200–400 мкг два раза в сутки. В периоды повышения тяжести течения бронхиальной астмы суточную дозу можно увеличить до 1600 мкг, назначаемых на несколько (два) приемов, и затем уменьшать после стабилизации течения астмы.
Дозирование один раз в сутки
Взрослым пациентам с бронхиальной астмой легкого и среднетяжелого течения (включая пожилых и детей/подростков старше 12 лет): у пациентов, ранее не получавших ингаляционные глюкокортикостероиды, поддерживающая доза обычно составляет 200–400 мкг один раз в сутки. У пациентов, у которых течение заболевания уже контролировалось ингаляционными глюкокортикостероидами (например, будесонидом или беклометазона дипропионатом), назначаемыми два раза в сутки, можно использовать ингаляции 800 мкг один раз в сутки. Детям 6–12 лет с бронхиальной астмой легкого или среднетяжелого течения: у пациентов, ранее не получавших терапии стероидами, а также у пациентов, у которых ингаляционные глюкокортикостероиды (например, будесонид или беклометазона дипропионат), назначаемые два раза в сутки, ранее позволяли контролировать течение заболевания, поддерживающая доза обычно составляет 200–400 мкг один раз в сутки. Пациента следует переводить на ингаляции препарата один раз в сутки в той же суточной дозе (учитывая особенности препарата и способ введения). После этого дозу следует снизить до минимальной, необходимой для обеспечения эффективного контроля течения бронхиальной астмы. Пациентов следует обучить принимать препарат один раз в сутки по вечерам. Важно, чтобы прием препарата был постоянным и проводился в одно и то же время по вечерам. Данных для выработки рекомендаций по переводу пациентов без предшествующей ингаляционной терапии глюкокортикостероидами на ингаляции препарата Будесонид Изихейлер один раз в сутки недостаточно. Пациентам, получающим препараты один раз в сутки, следует рекомендовать при ухудшении течения бронхиальной астмы (например, при повышении частоты пользования бронходилататорами или при сохранении симптомов со стороны органов дыхания) удваивать дозу принимаемых ими глюкокортикостероидов путем перехода на их ингаляции два раза в сутки. При этом пациентам следует рекомендовать как можно скорее обратиться к врачу.
У пациента постоянно под рукой должны быть ингаляционные бронходилататоры короткого действия, предназначенные для купирования приступов бронхиальной астмы.
При ХОБЛ доза подбирается врачом индивидуально в зависимости от тяжести заболевания. Рекомендуемые начальные дозы 100-400 мкг два раза в день. Наибольшая рекомендуемая доза 800 мкг два раза в день.
Ингалятор Изихейлер управляется потоком вдыхаемого воздуха. Это означает, что когда пациент вдыхает воздух через мундштук, лекарственное вещество поступает в дыхательные пути вместе с вдыхаемым воздухом.
Note
Важно обратить внимание пациента на следующее:
– после вскрытия ламинированной упаковки рекомендуется хранить устройство в защитном чехле, чтобы предотвратить повреждение Изихейлера в процессе использования и повысить его устойчивость к внешним воздействиям;
– встряхивать устройство и проводить пробное распыление порошка перед первым использованием;
– в положении сидя или стоя вдыхать через мундштук достаточно активно и глубоко, чтобы обеспечить поступление в бронхи оптимальной дозы вещества;
– не выдыхать через мундштук, поскольку это приведет к снижению поступающей в организм дозы. Если это все же произошло, необходимо постучать ингалятором по твердой поверхности или по ладони руки, чтобы извлечь порошок из мундштука, а затем повторить процедуру приёма препарата. Таким же образом необходимо поступать в случае, если пациент непреднамеренно включил ингалятор без последующего проведения ингаляции.
– всегда закрывать защитную крышку после использования ингалятора, чтобы предотвратить случайное распыление порошка из устройства (которое может привести либо к передозировке, либо к ингаляции недостаточного количества препарата при последующем использовании ингалятора);
– промывать рот водой или чистить зубы после ингаляции, чтобы свести к минимуму риск развития кандидоза полости рта и глотки, а также охриплости голоса;
– регулярно прочищать мундштук сухой тряпочкой. Для очищения нельзя использовать воду, поскольку порошок гигроскопичен;
– заменять ингалятор Будесонид Изихейлер, когда на счетчике появляется ноль, даже если внутри устройства все еще видно некоторое количество порошка.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | ORION |









There are no reviews yet.