- No products in the cart.
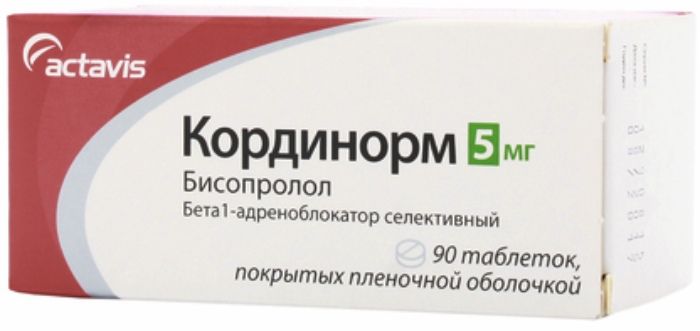
Renipril rm tabs 10mg + 12.5mg 20 pcs Pharmstandard
$2.49
Renipril rm tabs 10mg + 12.5mg 20 pcs Pharmstandard
SKU: 1230829810 Categories: Heart and blood vessels, High pressure, Medicaments Tags: enalapril + hydrochlorothiazide, Pharmstandard
Description
Composition
Active substance:
1 tablet contains: enalapril maleate 10 mg, hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg.
Excipients:
Potato starch – 59.3 mg, lactose monohydrate (milk sugar) – 111.5 mg, povidone (polyvinylpyrrolidone, low molecular weight Medical) – 4 mg colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil) – 0.7 mg of, calcium stearate (calcium stearate) – 2 mg.
Description:
Tablets white or white with kremovatam color, Valium with Valium and chamfered. On the surface of the tablet is supposed Valium.
Product form:
Tablets. At 10 or 20 tablets in blisters. 1, 2 or 3 blisters with instructions for use in a pack.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including the individual components of the preparation or sulfonamides); anuria expressed renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL / min); bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery to a solitary kidney; angioedema history associated with the use of ACE inhibitors, as well as idiopathic or hereditary angioneurotic edema; primary hyperaldosteronism; Addison’s disease; porphyria; pregnancy, lactation; age 18 years (effectiveness and safety have been established).
Precautions: renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance of 30-75 ml / min); expressed aortic stenosis or idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis; ischemic heart disease and cerebrovascular diseases (including cerebrovascular insufficiency); chronic heart failure; severe systemic autoimmune connective tissue disease (including systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma); inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis; diabetes; hyperkalemia; state after renal transplantation; severe liver function; state, accompanied by a decrease in blood volume (as a result of diuretic therapy, while limiting the consumption of salt, diarrhea or vomiting); elderly age; gout.
Dosage
12.5 mg + 10 mg
Indications
Hypertension (patients in whom combination therapy is shown).
Interaction with other drugs
Simultaneous treatment with other antihypertensive agents, barbiturates, tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines and drugs as well as alcohol intake, enhances the antihypertensive effect Renipril® GT.
Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a large amount of salt in the diet, simultaneous cholestyramine or colestipol reduce the effect Renipril® HT.
The simultaneous use of lithium therapy can lead to lithium intoxication, as enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide reduce excretion of lithium. Necessary to monitor the concentration of lithium in blood serum and its dosage adjustment. If possible, avoid simultaneous treatment Renipril® GT and lithium preparations.
Simultaneous use Renipril® HT and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics (by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis) may reduce the effectiveness of enalapril and increase the risk of deterioration of renal function and / or a heart failure. In some patients, while treatment may also decrease the antihypertensive effect of enalapril. Simultaneous treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, amiloride, triamterene) or addition of potassium can cause hyperkalemia.
The simultaneous appointment with allopurinol, cytostatics, systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents may cause leukopenia, anemia or pancytopenia, requiring periodic inspection of hemogram.
Care should be taken while using with cardiac glycosides.
Possible gidrohlorotiazidindutsirovannaya hypovolemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia may increase the toxicity of glycosides.
The simultaneous appointment with corticosteroids increases the risk of hypokalemia.
With simultaneous use of enalapril with theophylline may decrease the half-life of theophylline.
While the use of cimetidine may increase the half-life of enalapril. The risk of hypotension increases during application of general anesthesia or muscle relaxants nedepolyariziruyuschih (e.g., tubocurarine).
Overdose
Symptoms: increased diuresis, marked reduction in blood pressure with bradycardia or other cardiac arrhythmias, convulsions, paresis, paralytic ileus, impaired consciousness (including to whom), renal failure, acid-base balance, impaired electrolyte balance of blood.
Treatment: the patient is transferred to a horizontal position with a low headboard. In mild cases shown gastric lavage ingestion and brine, in more severe cases – actions to stabilize blood pressure – in / in a physiological saline solution, plasma expanders. The patient must monitor the level of blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, plasma concentrations of urea, creatinine, electrolytes and diuresis, if necessary – in / administration of angiotensin II, hemodialysis (enalaprilat elimination rate – 62 mL / min).
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Hypotensive combined means (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE) + diuretic).
Pharmacodynamics:
Renipril® HT is a combined preparation containing active substance: enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide, which effect is due to the properties of the components in its composition.
Enalapril – angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), is a “prodrug”: as a result of hydrolysis enalaprilat is formed, which inhibits ACE.
Hydrochlorothiazide – a thiazide diuretic. It acts at distal renal tubules, increasing the excretion of sodium and chloride ions. Early treatment hydrochlorothiazide fluid volume in the vessels is reduced by increasing the excretion of sodium and fluids, which leads to lower blood pressure (BP) and a decrease in cardiac output. With continued therapy antihypertensive effect of hydrochlorothiazide is based on reducing the total peripheral vascular resistance. Enalapril enhances the antihypertensive effect – inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, i.e. production of angiotensin II and its effects. Further decreases aldosterone production and enhances the effect of release of bradykinin and prostaglandins. As it often has its own diuretic effect, it can increase the effects of hydrochlorothiazide.
Enalapril reduces pre- and afterload, which unloads the left ventricle, leading to hypertrophy regression. As a result, the heart rate slows down and reduces the load on the heart (chronic heart failure), improves myocardial blood flow and decreased oxygen consumption cardiomyocytes. Thus, the reduced sensitivity of the heart to ischemia. It has a beneficial effect on cerebral blood flow in patients with arterial hypertension and chronic cardiovascular diseases. It prevents the development of glomerulosclerosis, maintains and improves renal function and slow even in those patients who have not yet developed hypertension during chronic kidney disease.
The antihypertensive effect of ACE higher in patients with hyponatremia inhibitors, hypovolemia, and elevated serum levels of renin, whereas the effect of hydrochlorothiazide is independent of renin in the blood serum. Therefore, co-administration of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide has the additional antihypertensive effect. Moreover, enalapril prevents or reduces the metabolic effects of diuretic therapy, and has a favorable effect on the structural changes in the heart and vessels.
Simultaneous administration of an ACE inhibitor and hydrochlorothiazide is used when each drug alone is insufficiently effective or monotherapy is conducted using the maximum dose of the drug that increases the incidence of adverse effects. The antihypertensive effect of the combination usually lasts for 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics:
Enalapril is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. suction volume is 60%. Food does not affect the absorption of enalapril. The maximum plasma concentration is reached after 1 hr. In the liver, enalapril is hydrolyzed to the active metabolite – enalaprilat. Enalaprilat maximum concentration in serum is attained after 3-6 hours. Enalapril displayed in the urine (60%) and the feces (33%) is preferably in the form of enalaprilat. Enalaprilat penetrates in most tissues of the body, mainly in the lungs, kidneys and blood vessels. Communication with plasma proteins – 50-60%. Renal clearance of enalapril and enalaprilat make 0,005 ml / s (18 l / h) and 0,00225-0,00264 ml / s (8,1-9,5 l / h), respectively. It appears in several stages. When assigning multiple doses of enalapril enalaprilat half-life of blood serum is approximately 11 hours. Enalapril and enalaprilat penetrate the placenta and are excreted in breast milk.
Enalaprilat removed from the blood by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis clearance enalaprilat 0,63-1,03 ml / s (38-62 ml / min); serum concentrations of enalaprilate After 4-hour hemodialysis reduced by 45-57%.
In patients with reduced renal function is slowing down, which requires a change in dosage according to renal function, especially in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Patients with liver failure enalapril metabolism can be slowed down, while its pharmacodynamic effect is not changed.
In patients with heart failure, absorption and metabolism slows enalaprilat, also reduced the volume of distribution.
Hydrochlorothiazide is absorbed mainly in the duodenum and proximal small intestine. The absorption is 70% and increases to 10% when taken with food. The level of the maximum serum concentration achieved after 1.5-5 hours. The volume of distribution of about 3 l / kg. Communication with plasma proteins – 40%. The drug accumulates in erythrocytes, accumulation mechanism is not known. It is not metabolized in the liver and excreted mainly by the kidneys 95% unchanged and about 4% as a hydrolyzate 2-amino-4-chloro-m-benzenedisulfonamida. Renal clearance of hydrochlorothiazide in healthy volunteers and patients with hypertension of approximately 5.58 ml / s (335 ml / min). Hydrochlorothiazide is a biphasic profile excretion. The half-life (T1 / 2) in the initial phase of 2 hours, in the final phase (10-12 h after administration) -. About 10 hours penetrates the placental barrier and accumulate in the amniotic fluid. Serum concentration of hydrochlorothiazide in the umbilical vein is essentially the same as in the maternal blood. in amniotic fluid concentration exceeds that in serum from umbilical vein (19 times). The level of hydrochlorothiazide in breast milk is very low.
When assigning hydrochlorothiazide in patients with heart failure found that its absorption decreases proportionally to the degree of the disease – 20-70%. T1 / 2 of hydrochlorothiazide is increased to 28.9 hours; renal clearance is 0,17-3,12 ml / sec (10-187 mL / min) (mean values of 1.28 ml / s (77 ml / min)).
In patients undergoing surgery of the intestinal bypass surgery for obesity, the absorption of hydrochlorothiazide may be reduced by 30% and the serum concentration of 50%, than in healthy volunteers.
The simultaneous appointment of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of each of them.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
The drug is contraindicated in pregnancy. When pregnancy occurs the drug should be discontinued immediately. If necessary, the appointment during lactation nursing mothers should abandon breastfeeding.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
On prescription.
side effects
General weakness, hypersensitivity reactions, necrotizing vasculitis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema.
Cardio-vascular system: palpitations, fainting, chest pain, a variety of cardiac arrhythmias, marked reduction in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension.
On the part of the digestive tract: dry mouth, glossitis, stomatitis, an inflammation of the salivary glands, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, epigastric pain, intestinal colic, ileus, pancreatitis, hepatic failure, hepatitis, jaundice.
The respiratory system: nonproductive “dry” cough, rhinitis, sinusitis, sore throat, hoarseness, bronchospasm, eosinophilic pneumonia.
From the urogenital system: oliguria, gynecomastia, decreased potency, decreased libido, renal insufficiency, renal failure, interstitial nephritis.
Allergic reactions: angioedema (face, tongue, lips, vocal cords, larynx, limbs, intestine), sweating, exfoliative dermatitis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
For the skin: skin rash, pruritus, alopecia.
From the senses: blurred vision, taste disturbance, impaired sense of smell, tinnitus, conjunctivitis.
Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, fatigue, depression, ataxia, fatigue, drowsiness, insomnia, anxiety, nervousness, peripheral neuropathy (paresthesia, dysesthesia).
Laboratory findings: hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, gipohloremichesky alkalosis, hyperglycemia, hypercreatininemia, hyper- or hypokalemia, glycosuria, hyperuricemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, increased activity of “liver” enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia, leukocytosis, eosinophilia, neutropenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, anemia, pancytopenia, decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Miscellaneous: lupus-like syndrome (fever, myalgias / myositis and arthralgia / arthritis, serositis, vasculitis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, positive test for antinuclear antibodies), photosensitivity, muscle cramps.
special instructions
Marked reduction in blood pressure with all the clinical effects may be observed after the first dose of pills Renipril® HT in patients with severe heart failure and hyponatremia, severe renal failure, left ventricular dysfunction and, in particular, in patients who are in a state of hypovolemia due to diuretic therapy, salt-free diet, diarrhea, vomiting or hemodialysis. Hypotension after the first dose and its more serious consequences is a rare and passing phenomenon. It is possible to avoid the cancellation of a diuretic, if possible, before beginning treatment Renipril® GT.
In case of hypotension patients must be laid on its back with a low headboard and if necessary to adjust the volume of the plasma by infusion of saline. Transient hypotension is not a contraindication to further treatment. After normalization of blood pressure and volume replacement patients usually tolerate subsequent doses.
Caution is needed when using in patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance of 0.5 to 1.3 ml / s). Patients taking hydrochlorothiazide, may develop azotemia. In patients with impaired renal function may show signs of accumulation of the drug. If necessary, it can be used a combination of enalapril with a lower amount of hydrochlorothiazide or combination therapy with enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide should be canceled.
Requires regular monitoring of serum electrolytes during treatment to detect possible imbalance. Determination of serum electrolytes is necessary for patients with prolonged diarrhea, vomiting and receiving intravenous infusion.
Patients taking Renipril® GT, signs need to be identified electrolyte imbalance, such as dry mouth, thirst, weakness, drowsiness, lethargy, agitation, muscle pain or cramps (mainly calf muscle), decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, oliguria and gastrointestinal gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting).
During treatment Renipril® HT hypomagnesemia can be observed and sometimes hypercalcemia resulting magnesium excretion increasing deceleration and calcium excretion in urine under the effect of hydrochlorothiazide. A significant increase in serum levels of calcium can be an indication of latent hyperparathyroidism. In some patients, as a result of hydrochlorothiazide may experience worsening of hyperuricemia or gout. If the rise is noted the concentration of uric acid in blood serum, the treatment should be discontinued. It may be resumed after the normalization of laboratory values and in the future, be carried out under their control. Caution is required in all patients receiving treatment with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin, as hydrochlorothiazide may weaken, and enalapril to strengthen their action. Patients with diabetes should be seen more often, and may require some change in the dose of hypoglycemic agents if necessary. If you experience angioedema face or neck is usually sufficient to cancel the therapy and administering to the patient antihistamines. In more severe cases (edema tongue, pharynx and larynx) angioedema treated with adrenaline, it is necessary to maintain the airway (intubation or thyroidotomy). Антигипертензивный эффект Рениприл® ГT может усиливаться после симпатэктомии. Вследствие повышения риска анафилактических реакций не следует назначать Рениприл® ГТ пациентам, находящимся на гемодиализе с использованием полиакрилонитриловых мембран, подвергающихся аферезу с декстрансульфатом и непосредственно перед процедурой десенсибилизации к осиному или пчелиному яду.
Во время лечения Рениприл® ГТ могут отмечаться реакции повышенной чувствительности у пациентов без предшествующей аллергии или бронхиальной астмы. Сообщалось об ухудшении течения системной красной волчанки.
При возникновении желтухи и повышении активности “печеночных” ферментов лечение должно быть немедленно прекращено, пациенты должны находиться под наблюдением.
Осторожность также необходима у пациентов, принимающих сульфонамиды или пероральные гипогликемические средства из группы сульфонилмочевины (возможна перекрестная повышенная чувствительность).
Во время лечения требуется периодический контроль количества лейкоцитов, особенно у пациентов с заболеваниями соединительной ткани или почек.
Во время лечения необходим периодический контроль сывороточной концентрации электролитов, глюкозы, мочевины, креатинина и активности “печеночных” ферментов, а также белка мочи. Лечение Рениприл® ГТ должно быть прекращено перед проведением исследований функции паращитовидных желез.
Impact on the ability to drive a car and mechanisms
У некоторых пациентов преимущественно в начале лечения могут возникать артериальная гипотензия и головокружение, что может снижать способность к управлению автомобилем и работе с механизмами. В начале лечения рекомендуется избегать работы, требующей концентрации внимания, до тех пор, пока не будет установлен ответ на лечение.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not higher than 25 C. Keep out of reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Лечение артериальной гипертензии не начинают с комбинации лекарственных средств. Первоначально должны быть определены адекватные дозы отдельных компонентов. Дозировка всегда должна подбираться индивидуально для каждого пациента.
Обычная доза – 1 таблетка в сутки. Пациенты должны принимать таблетки целиком во время или после еды, запивая небольшим количеством жидкости, предпочтительно утром. В случае пропуска приема очередной дозы препарата, ее необходимо принять как можно скорее, если до приема следующей дозы осталось достаточно большое количество времени. Если до приема последующей дозы осталось несколько часов, следует подождать и принять только ее. Никогда не следует удваивать дозу.
Если не достигается удовлетворительный терапевтический эффект, рекомендуется добавить другое лекарственное средство или изменить терапию.
У пациентов, находящихся на терапии диуретиками, рекомендуется отменить лечение или снизить дозу диуретиков как минимум за 3 дня до начала лечения Рениприл® ГТ для предотвращения развития симптоматической гипотензии. Перед началом лечения должна быть исследована функция почек.
Дозировка при нарушенной функции почек
Пациентам с клиренсом креатинина более 0,5 мл/с или сывороточным креатинином менее 265 моль/л (3 мг/100 мл) может быть назначена обычная доза Рениприл® ГТ.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard |










There are no reviews yet.