- No products in the cart.
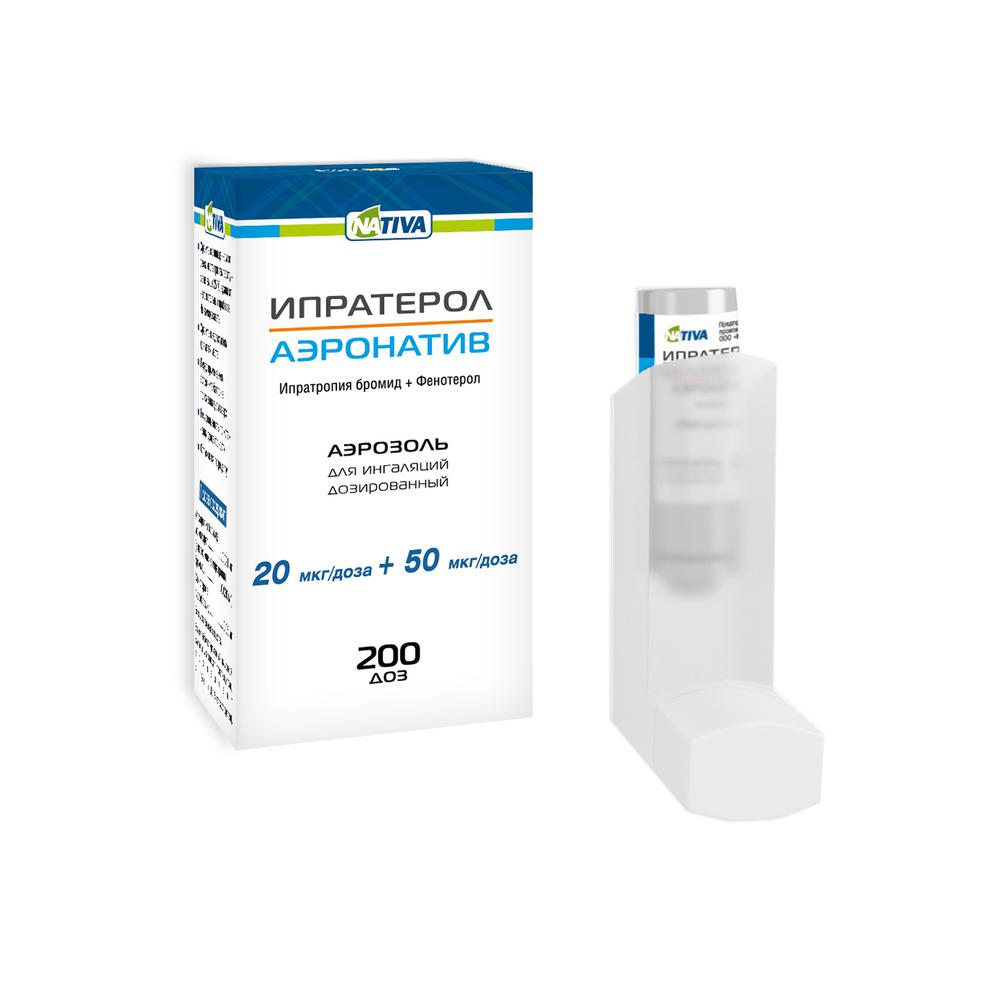
Ipraterol aeronativ spray-ing. scrapper. 20mkg 50mkg + / dose

Solgar lozenges 50 pcs Flavio zinc
$14.54
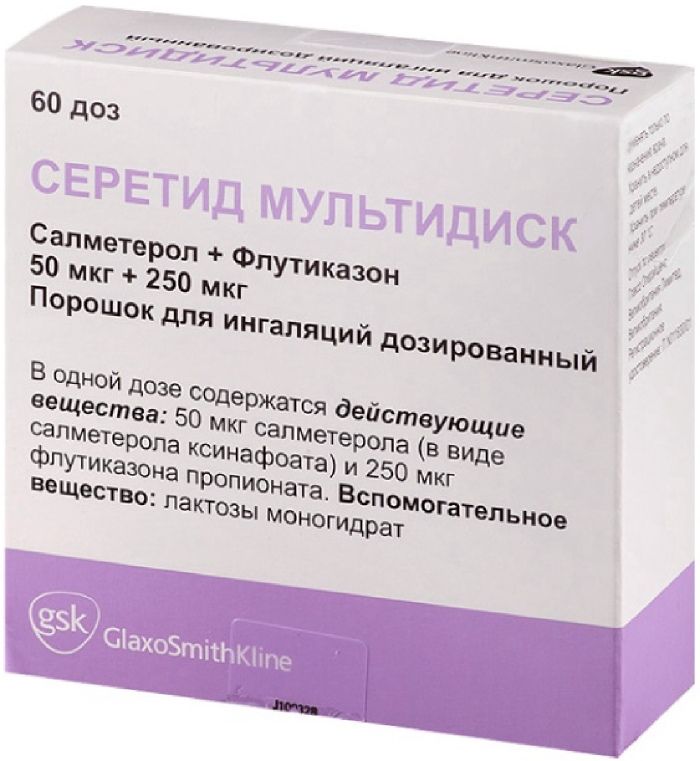
Seretide multidisk powder ing.dozir. 50mkg / 250mkg 60doz with inhaler
$33.31
$9.81
Ipraterol aeronativ spray-ing. scrapper. 20mkg 50mkg + / dose
SKU: 0694969104 Categories: Bronchial asthma, COPD, Medicaments Tags: fenoterol +, FT SYNTHESIS, Ipratropium bromide
Description
Composition
Active substance:
Ipratropium bromide monohydrate 0.021 mg (based on the ipratropium bromide) (0.020 mg)
Fenoterol hydrobromide 0.050 mg.
Excipients:
Ethanol, absolute 15,300 mg
Citric acid monohydrate 0.005 mg
Triethyl citrate 0.150 mg
R Propellant 134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) 44.470 mg.
Description:
Colorless or with slight yellowish tinge clear solution, which is under pressure in the cylinder of stainless steel with a metering valve and a spray nozzle action; preparation at the outlet of the container is sprayed in the form of an aerosol jet.
Product form:
Aerosol for inhalation dose, 20 .mu.g / dose + 50 .mu.g / dose.
200 doses of the drug in the cylinder of stainless steel with a metering valve and a spray nozzle action. Each cylinder together with instructions for use in a cardboard package.
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to fenoterol, ipratropium bromide (as well as other drugs atropine) and the auxiliary components within the preparation. • Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. • Tachyarrhythmia. • The first trimester of pregnancy. • Children up to age 6 years.
Carefully
Preparation Ipraterol-aeronativ should be used with caution in patients with diseases such as the angle-closure glaucoma, hypertension, diabetes, recent myocardial infarction (within the last 3 months), heart and vascular diseases, such as chronic heart failure, coronary heart disease , arrhythmias, aortic stenosis, marked the defeat of cerebral and peripheral artery disease, hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma, prostatic hyperplasia, bladder neck obstruction, th kovistsidoz, II and III trimesters of pregnancy, lactation. The drug-Ipraterol aeronativ should be used with caution in children and adolescents aged 6 to 18 years.
Dosage
20 .mu.g + 50 pg / dose
Indications
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, emphysema, bronchial asthma (mild and moderate).
Interaction with other drugs
Prolonged simultaneous use of the drug-Ipraterol aeronativ with other anticholinergic drugs is not recommended due to lack of data.
The simultaneous use of other beta-adrenomimeticheskih and anticholinergic drugs, including systemic effects, and xanthine derivatives (e.g., theophylline) may enhance bronchodilatory action Ipraterol- aeronativ drug and lead to increased unwanted reactions.
Perhaps a significant weakening of bronchodilator action Ipraterol- drug aeronativ with concomitant administration of beta-blockers.
Hypokalemia associated with beta-agonists, can be enhanced while appointment xanthine derivatives, glucocorticoids, and diuretics. This fact should be given special attention in the treatment of patients with severe obstructive airways disease. Hypokalemia may increase the risk of arrhythmias in patients receiving digoxin.
Additionally, hypoxia may exacerbate the negative effect of hypokalaemia on cardiac rhythm. In such cases, it is recommended to carry out monitoring of the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma.
It should be used with caution beta2-adrenergic drugs patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and tricyclic antidepressants, since these drugs can enhance the effect of beta-adrenergic agents.
Inhalation agents for general anesthesia such as a halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetics (halothane, trichlorethylene, enflurane), may enhance the adverse effect of beta-adrenergic agents to the cardiovascular system.
The combined use of the drug with cromoglicic acid and / or increases the efficiency of therapy with glucocorticosteroids.
Overdose
symptoms
Overdose symptoms typically associated with the action of fenoterol. Perhaps the appearance of symptoms caused by excessive stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. The most likely occurrence of tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, hypertension or hypotension, increasing the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure, increased pulse pressure, increased stenokardicheskie pain, arrhythmia, and a sense of “tides” of blood to the face, metabolic acidosis, hypokalemia, a feeling of heaviness behind the sternum, increased bronchial obstruction.
Possible overdose symptoms of ipratropium bromide (such as dry mouth, accommodation disturbance Eye), considering the great breadth of therapeutic action of the drug and the local way of application, generally mild and transient in nature are.
Treatment
You need to stop taking the drug Ipraterol-aeronativ. Should take into account monitoring data of acid-base balance of blood. It recommended the appointment of sedative drugs, anxiolytic drugs (tranquilizers), in severe cases – intensive care.
As a specific antidote possible use of beta-blockers, preferably selective beta1-adrenergic blockers. However, be aware of the possible strengthening of bronchial obstruction under the influence of beta-blockers and carefully select a dose for patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease because of the risk of severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Bronchodilatory agent combined (beta 2- adrenoagonists selective-holinoblokator + m).
Pharmacodynamics:
The drug-Ipraterol aeronativ comprises two components having bronchodilating activity: ipratropium bromide – m-holinoblokator and fenoterol – beta2-agonists.
Bronchodilation when inhaled ipratropium bromide is mainly due to local rather than systemic anticholinergic effects.
Ipratropium bromide is a quaternary ammonium derivatives having anticholinergic (parasympatholytic) properties. Ipratropium bromide inhibits the reflexes caused by the vagus nerve. Anticholinergics prevent the increase in intracellular calcium ion concentration that occurs due to the interaction with muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of bronchial smooth muscle.
The release of calcium ions is mediated by the system of secondary mediators, which include inositol triphosphate (ITP) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
In patients with bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis and emphysema), significant improvements in lung function (increase in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and peak expiratory flow rate (PSV) of 15% or more) is marked for 15 minutes, the maximum effect is achieved after 1-2 hours and lasts until the majority of patients 6 hours after administration.
Ipratropium bromide has no adverse effect on mucus secretion in airway mucociliary clearance and gas exchange.
Fenoterol selectively stimulates beta2-adrenergic receptors in the therapeutic dose. Beta1- adrenoceptor stimulation occurs at high doses. Fenoterol relaxes the smooth muscles of bronchi and vessels and prevents the development of bronchospastic reactions, caused by histamine, methacholine, cold air and allergens (immediate hypersensitivity reaction). Immediately after administration of fenoterol blocking the release of mediators of inflammation and bronchial mast cell. Furthermore, when using fenoterol at doses of 0.6 mg, it was noted enhancement of mucociliary clearance.
Beta adrenergic (beta-adrenoceptor stimulating) effect of the drug on cardiac activity, such as increased frequency and severity of cardiac contractions, due to the action of vascular fenoterol, beta2-adrenergic stimulation of the heart, and at doses exceeding therapeutic, beta1-adrenoceptor stimulation. As with other beta-adrenergic drugs is marked prolongation of the interval QTc at high doses. When using fenoterol via aerosol metered dose inhalers (MDIs), this effect was unstable and was observed in the case of doses exceeding recommended. However, after applying fenoterol using nebulizers (for the inhalation solution in vials with standard dose) systemic exposure may be higher than when using the drug by MDI at recommended doses. The clinical significance of these observations is not established. Most often nayulyudaemym effect of beta-adrenergic agonists is tremor. In contrast to the effects on the bronchial smooth muscle, to the systemic effects of beta-adrenergic agonists may develop tolerance, the clinical significance of this manifestation is not clear. Tremor is the most common adverse effect of using beta-adrenoceptor agonists. In joint use of these two active substances bronchodilatory effect is achieved by acting on different pharmacological targets. These substances complement each other, resulting in enhanced spasmolytic effect on the bronchial muscle and provides greater latitude therapeutic action in bronchopulmonary diseases involving airway constriction. The complementary action is such that to achieve the desired effect requires a lower dose of beta-adrenergic component that enables individually choose an effective dose in the substantial absence of side effects.
In acute bronchoconstriction effect of the drug is rapidly developing, it can be used for acute attacks of bronchospasm.
Pharmacokinetics:
There is no evidence that the pharmacokinetics combined preparation comprising ipratropium bromide and fenoterol, differs from that of each of the individual components.
Suction
Inhalation administration route for ipratropium bromide is characterized by very low absorption from the respiratory tract mucosa. The concentration of ipratropium bromide in blood plasma is at the lower boundary definition, and it can be measured only at high doses deyustvuyuschego substance. After inhalation to the lung is usually misses (depending upon the dosage form and the method of inhalation) 10-30% of the administered dose of ipratropium bromide. Most of the dose is swallowed and enters the gastrointestinal tract.
Part dose ipratropium bromide, entering the lungs rapidly reaches the systemic circulation (within several minutes). The total systemic bioavailability of ipratropium bromide inhalation applied is 2% and 7-28%, respectively.
Depending on the method used by inhalation and inhalation system of about 10-30% of fenoterol reaches the lower airways, and the remainder is deposited in the upper airways and is swallowed. As a result, a certain amount of inhaled fenoterol enters the gastrointestinal tract. Suction is biphasic – 30% of fenoterol is rapidly absorbed with a half-life (T1 / 2) 11 minutes and 70% slowly absorbed T1 / 2 – 120 minutes. There is no correlation between the concentrations of fenoterol in blood plasma is achieved after inhalation, and pharmacodynamic curve “time effect”.
Long (3-5 hours) bronchodilatory effect after inhalation of the drug that is comparable with the respective effects achieved after intravenous administration, is not supported fenoterol high concentrations in the systemic circulation. After oral administration absorbed about 60% of fenoterol. Time of maximum plasma concentration is 2 hour.
Distribution
Ipratropium bromide, a quaternary amine which is poorly soluble in fats and weakly penetrates through biological membranes. Not accumulates. Ipratropium bromide binds to plasma proteins to a minimum extent (less than 20%). No information about the possibility of penetration of ipratropium bromide through the placental barrier and into breast milk.
Fenoterol is distributed rapidly to organs and tissues. Communication with the plasma proteins is 40-55%. Fenoterol unaltered cross the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
There is no evidence that the pharmacokinetics combined preparation comprising ipratropium bromide and fenoterol, differs from that of each of the individual components.
Suction
Inhalation administration route for ipratropium bromide is characterized by very low absorption from the respiratory tract mucosa. The concentration of ipratropium bromide in blood plasma is at the lower boundary definition, and it can be measured only at high doses deyustvuyuschego substance. After inhalation to the lung is usually misses (depending upon the dosage form and the method of inhalation) 10-30% of the administered dose of ipratropium bromide. Most of the dose is swallowed and enters the gastrointestinal tract.
Part dose ipratropium bromide, entering the lungs rapidly reaches the systemic circulation (within several minutes). The total systemic bioavailability of ipratropium bromide inhalation applied is 2% and 7-28%, respectively.
Depending on the method used by inhalation and inhalation system of about 10-30% of fenoterol reaches the lower airways, and the remainder is deposited in the upper airways and is swallowed. As a result, a certain amount of inhaled fenoterol enters the gastrointestinal tract. Suction is biphasic – 30% of fenoterol is rapidly absorbed with a half-life (T1 / 2) 11 minutes and 70% slowly absorbed T1 / 2 – 120 minutes. There is no correlation between the concentrations of fenoterol in blood plasma is achieved after inhalation, and pharmacodynamic curve “time effect”. Long (3-5 hours) bronchodilatory effect after inhalation of the drug that is comparable with the respective effects achieved after intravenous administration, is not supported fenoterol high concentrations in the systemic circulation. After oral administration absorbed about 60% of fenoterol. Time of maximum plasma concentration is 2 hour.
Distribution
Ipratropium bromide, a quaternary amine which is poorly soluble in fats and weakly penetrates through biological membranes. Not accumulates. Ipratropium bromide binds to plasma proteins to a minimum extent (less than 20%). No information about the possibility of penetration of ipratropium bromide through the placental barrier and into breast milk.
Fenoterol is distributed rapidly to organs and tissues. Communication with the plasma proteins is 40-55%. Fenoterol unaltered cross the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism
Ipratropium bromide is metabolized by oxidation primarily in the liver.
It is known to 8 ipratropium bromide metabolites, which are poorly bind to muscarinic receptors and are considered inactive.
Fenoterol metabolized in the liver. After 24 hours 60% of the intravenously administered dose and 35% of an oral dose is excreted in the urine. This fraction fenoterol biotransformation due to “first-pass” effect through the liver, resulting in drug bioavailability after oral administration of drops to about 1.5%. This explains the fact that the amount of drug swallowed virtually no effect on the concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma is reached after inhalation. Biotransformation of fenoterol in man occurs principally by conjugation with sulphates in the intestinal wall.
breeding
Ipratropium bromide is derived mainly through the intestine and through the kidneys.
About 25% is excreted unchanged in the rest – in the form of metabolites.
Fenoterol excreted by the kidneys and in bile as inactive sulfate conjugates. In parenteral administration, fenoterol respectively output three-phase model with half-lives – 0.42 minutes, 14.3 minutes and 3.2 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in specific patient groups
Pharmacokinetics combined preparation comprising ipratropium bromide and fenoterol, patients with diabetes, patients of advanced age and older and children, and in patients with impaired hepatic and renal function was not studied.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
These pre-clinical studies and the current clinical experience with the combination of fenoterol and ipratropium bromide showed that the active ingredients that make up the combination product, no adverse effects during pregnancy. It is necessary to consider the possibility of an inhibitory action of fenoterol on uterine activity. The drug-Ipraterol aeronativ contraindicated in I trimester of pregnancy (possible weakening of labor). Caution is advised to use the drug in aeronativ Ipraterol-II and III trimester of pregnancy.
Fenoterol passes into breast milk. Evidence that ipratropium bromide passes into breast milk have not been received. Safety of the drug during breast-feeding has not been established. In connection with this use of the drug
Ipraterol-aeronativ lactation is possible only when the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the child’s mother.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Prescription.
side effects
Many of the listed undesirable effects can be caused by anticholinergics and beta-adrenergic properties Ipraterol-aeronativ drug. Применение препарата
Ипратерол-аэронатив, как и любая ингаляционная терапия, может вызвать местное раздражение.
Определение частоты: очень часто (>1/10), часто (от 1/100 до 1/10), нечасто (от 1/1000 до 1/100), редко (от 1/10000 до 1/1000), очень редко (
Нарушения со стороны иммунной системы: редко – реакции гиперчувствительности, анафилактические реакции (отек Квинке).
Нарушения со стороны обмена веществ и питания: редко – гипокалиемия.
Нарушения психики: нечасто – нервозность; редко – чувство беспокойства, ментальные нарушения (психические растройства).
Нарушения со стороны нервной системы: нечасто – головная боль, головокружение, тремор.
Нарушения со стороны органа зрения: редко – глаукома, увеличение внутриглазного давления, нарушения аккомодации, мидриаз, затуманивание зрения, боль в глазах, отек роговицы, гиперемия конъюнктивы, появление ореола вокруг предметов и цветных пятен перед глазами.
Нарушения со стороны сердца: нечасто – тахикардия, ощущение сердцебиения; редко – аритмия, мерцательная аритмия, фибрилляция предсердий, наджелудочковая тахикардия, ишемия миокарда.
Нарушения со стороны дыхательной системы, органов грудной клетки и средостения: часто – кашель; нечасто – фарингит, дисфония; редко – бронхоспазм, раздражение глотки, отек глотки, ларингоспазм, парадоксальный бронхоспазм, сухость глотки.
Нарушения со стороны желудочно-кишечного тракта: нечасто – рвота, сухость во рту, тошнота; редко – стоматит, глоссит, нарушения моторики желудочно-кишечного тракта, диарея, запор, отек полости рта.
Нарушения со стороны кожи и подкожных тканей: редко – крапивница, кожная сыпь, зуд, потливость.
Нарушения со стороны скелетно-мышечной и соединительной ткани: редко – мышечная слабость, миалгии (боли в мышцах), спазм мышц.
Нарушения со стороны почек и мочевыводящих путей: редко – задержка мочи. Лабораторные и инструментальные данные: нечасто – повышение систолического артериального давления; редко – повышение и понижение диастолического артериального давления.
Если любые из указанных в инструкции побочных эффектов усугубляются или Вы заметили любые другие побочные эффекты, не указанные в инструкции, сообщите об этом врачу.
special instructions
В случае неожиданного быстрого усиления одышки (затруднений дыхания) следует немедленно обратиться к врачу.
У детей препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив следует применять только по назначению врача и под контролем взрослых. Применение у детей младше 6 лет противопоказано, в связи с отсутствием опыта применения.
Hypersensitivity
После применения препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив могут возникнуть реакции немедленной гиперчувствительности, признаками которой в редких случаях могут быть: крапивница, ангионевротический отек, сыпь, бронхоспазм, отек ротоглотки, анафилактический шок.
paradoxical bronchospasm
Препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив, как и другие ингаляционные лекарственные средства, способен вызвать парадоксальный бронхоспазм, который может угрожать жизни. В случае развития парадоксального бронхоспазма применение препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив следует немедленно прекратить и перейти на альтернативную терапию.
Длительное применение – у пациентов с бронхиальной астмой препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив должен применяться только по мере необходимости; у пациентов с ХОБЛ легкой степени тяжести симптоматическое лечение может оказаться предпочтительнее регулярного применения; – у пациентов, страдающих бронхиальной астмой, следует помнить о необходимости проведения или усиления противовоспалительной терапии для контроля воспалительного процесса дыхательных путей и течения заболевания.
Регулярное применение возрастающих доз лекарственных средств, содержащих бета2-адреномиметики, таких как препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив, для купирования бронхиальной обструкции может вызвать неконтролируемое ухудшение течения заболевания. В случае усиления бронхиальной обструкции увеличение дозы бета2- адреномиметиков, в том числе препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив, больше рекомендуемой в течение длительного времени не только не оправдано, но и опасно. Для предотвращения угрожающего жизни ухудшения течения заболевания следует рассмотреть вопрос о пересмотре плана лечения пациента и адекватной противовоспалительной терапии ингаляционными глюкокортикостероидами.
Другие симпатомиметические бронходилататоры следует назначать одновременно с препаратом Ипратерол-аэронатив только под медицинским наблюдением.
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract
У пациентов, имеющих в анамнезе муковисцидоз, возможны нарушения моторики желудочно-кишечного тракта.
Violations by the organ of vision
Препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив должен применяться с осторожностью у пациентов, предрасположенных к закрытоугольной глаукоме. Известны отдельные сообщения об осложнениях со стороны органа зрения (например, повышение внутриглазного давления, мидриаз, закрытоугольная глаукома, боль в глазах), развившихся при попадании ингаляционного ипратропия бромида (или ипратропия бромида в сочетании с бета2- адреномиметиками) в глаза. Симптомами острой закрытоугольной глаукомы могут быть боль или дискомфорт в глазах, затуманивание зрения, появление ореола вокруг предметов и цветных пятен перед глазами в сочетании с отеком роговицы и покраснением глаз вследствие гиперемии конъюнктивы. Если развивается любая совокупность этих симптомов, показано применение глазных капель, снижающих внутриглазное давление, и немедленная консультация специалиста. Пациенты должны быть проинструктированы о правильном применении ингаляционного препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив. Для предупреждения попадания раствора в глаза рекомендуется, чтобы раствор, используемый с помощью небулайзера, вдыхался через мундштук. При отсутствии мундштука должна использоваться плотно прилегающая к лицу маска. Особенно тщательно должны заботиться о защите глаз пациенты, предрасположенные к развитию глаукомы.
Системные эффекты
При таких заболеваниях, как недавно перенесенный инфаркт миокарда, сахарный диабет с неадекватным гликемическим контролем, тяжело протекающие органические заболевания сердца и сосудов, гипертиреоз, феохромоцитома или обструкция мочеиспускательных путей (например, при гиперплазии предстательной железы или обструкции шейки мочевого пузыря) препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив должен применяться только после тщательной оценки риск/польза, особенно при использовании доз, превышающих рекомендуемые.
Влияние на сердечно-сосудистую систему
Отмечались редкие случаи возникновения ишемии миокарда при приеме бета
Гипокалиемия
При применении бета2-адреномиметиков может возникать гипокалиемия (см. раздел «Передозировка»). У спортсменов применение препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив в связи с наличием в его составе фенотерола может приводить к положительным результатам тестов на допинг. 2- адреномиметиков. Пациентов с сопутствующими серьезными заболеваниями сердца (например, ишемической болезнью сердца, аритмиями или выраженной сердечной недостаточностью), получающих препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив, следует предупреждать о необходимости обращения к врачу в случае появления болей в сердце или других симптомов, указывающих на ухудшение заболевания сердца. Необходимо обращать внимание на такие симптомы, как одышка и боль в груди, так как они могут быть как сердечной, так и легочной этиологии.
Effect on the ability to drive mechanisms and
Исследований влияния комбинированного препарата, содержащего ипратропия бромид и фенотерол, на способность к управлению транспортными средствами и механизмами не проводилось. Поскольку при применении препарата возможно развитие таких нежелательных реакций, как головокружение, нервозность, тремор, нарушение аккомодации глаз, мидриаз и затуманивание зрения, следует соблюдать осторожность при управлении транспортными средствами и механизмами, а также при занятиях другими потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенной концентрации внимания и быстроты психомоторных реакций.
Storage conditions
В защищенном от света месте при температуре не выше 25°С, вдали от нагревательных приборов. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Дозу следует подбирать индивидуально.
При отсутствии иных указаний врача рекомендуется применение следующих доз:
Adults and children over 6 years
Лечение приступов
В большинстве случаев для купирования симптомов достаточно двух ингаляционных доз аэрозоля. Если в течение 5 минут облегчения дыхания не наступило, можно использовать дополнительно 2 ингаляционные дозы.
Если эффект отсутствует после 4 ингаляционных доз, и требуются дополнительные ингаляции, следует немедленно обратиться за медицинской помощью.
Прерывистая и длительная терапия
По 1-2 ингаляции на один прием, до 8 ингаляций в сутки (в среднем по 1-2 ингаляции 3 раза в сутки). При бронхиальной астме препарат должен применяться только по мере необходимости.
Препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив у детей следует применять только по назначению врача и под контролем взрослых (см. раздел «Особые указания»).
Инструкция по проведению ингаляций
Пациенты должны быть инструктированы о правильном использовании дозированного аэрозоля.
Препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив предназначен только для ингаляционного применения.
Перед первым использованием ингалятора или если ингалятором не пользовались неделю и дольше проверьте его работу. Для этого снимите защитный колпачок с мундштука ингалятора, хорошо встряхните ингалятор и нажмите на баллон, выпуская одну струю препарата в воздух.
Проведение ингаляции
Шаг 1. Снимите защитный колпачок с мундштука ингалятора
Шаг 2. Энергично потрясите ингалятор.
Шаг 3. Сделайте медленный, полный выдох. Не выдыхайте в ингалятор!
Шаг 4. Удерживая баллон, как показано на рисунке 2, плотно обхватите губами мундштук.
Баллон должен быть направлен дном вверх!
Шаг 5. Выполните максимально глубокий вдох, одновременно быстро нажмите на дно баллона до высвобождения одной ингаляционной дозы.
Шаг 6. На несколько секунд задержите дыхание, затем выньте мундштук изо рта и медленно выдохните через нос.
Шаг 7. Наденьте защитный колпачок на мундштук ингалятора.
Повторите шаги 2-6 для получения второй ингаляционной дозы, если это необходимо.
Чистка ингалятора
Регулярно (раз в неделю) следует промывать мундштук ингалятора
Выньте металлический баллончик из пластикового футляра и сполосните футляр и колпачок теплой водой. Do not use the hot water. Тщательно высушите, но не используйте для этого нагревательные устройства. Поместите баллончик обратно в футляр и наденьте колпачок. Не погружайте металлический баллончик в воду.
The balloon is designed for 200 inhalations. После этого баллон следует заменить.
Применение препарата у детей должно проходить под контролем взрослых.
Рекомендуется для предотвращения вдоха через нос во время ингаляции зажимать ноздри ребенка.
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ: пластиковый мундштук для рта разработан специально для препарата Ипратерол-аэронатив и служит для точного дозирования препарата. The mouthpiece should not be used with other metered aerosol. Также нельзя использовать препарат Ипратерол-аэронатив с какими-либо другими адаптерами, кроме мундштука, поставляемого вместе с препаратом.
The cylinder is pressurized. Баллон нельзя вскрывать и подвергать нагреванию выше 50 °С!.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | FT SYNTHESIS |









There are no reviews yet.