- No products in the cart.
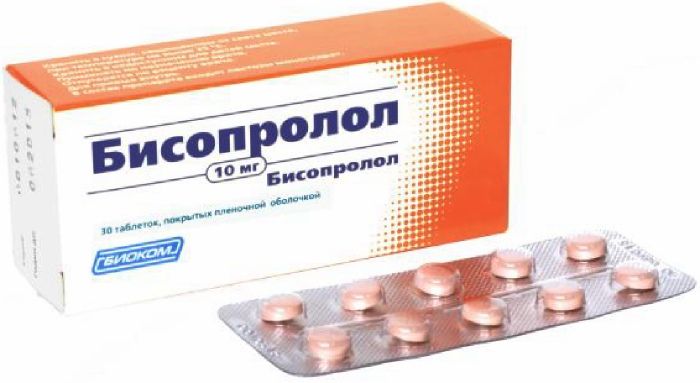
Bisoprolol tab p / 10 mg of the film 30 pcs Biocom
$2.64
Bisoprolol tab p / 10 mg of the film 30 pcs Biocom
SKU: 01877737252 Categories: Heart and blood vessels, High pressure, Medicaments Tags: bisoprolol, SYNTHESIS
Description
Composition
Active substance:
Bisoprolol fumarate – 0.01 g ,.
Excipients:
Lactose monohydrate (milk sugar) – 0.0973 g, or 0.0923 g of calcium carbonate – 0.0145 g Microcrystalline cellulose – 0.0145 g croscarmellose sodium (primelloza) – 0.0029 g talc – 0.00435 g magnesium stearate – 0.00145 g; shell composition: Opadry II White (polyvinyl alcohol – 40% titanium dioxide – 25% talc – 20.2%, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) – 14.8%) – 0.004737 g dyestuff iron oxide red E 172 – 0 , 000052 g, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) – 0.000052 g silicone emulsion – 0.000159 g
Description:
Tablets, film-coated, pink with slight brownish color, round, biconvex. Slight surface roughness. Color tablet in cross section from white to pale yellow.
Product form:
Tablets, film-coated 10mg.
10 tablets in blisters.
1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 contour cell packages together with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to bisoprolol or any of the components of the drug (see “Composition”.) – acute heart failure, CHF decompensation requiring holding inotropic therapy – cardiogenic shock, – atrioventricular (AV) block II and III degree, without a pacemaker, – sick sinus syndrome – sinoatrial block – bradycardia (heart rate less than 60 beats / min.) – marked hypotension (systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg..) – severe bronchial asthma – Intensity s violations of peripheral blood circulation, or Raynaud’s syndrome – pheochromocytoma (without the simultaneous use of alpha-blockers) – metabolic acidosis – the age of 18 years (lack of data on efficacy and safety in this age group).
Carefully
Conducting desensitizing therapy, Prinzmetal angina, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus I type and diabetes with considerable fluctuations in blood glucose concentration, AV block I degree, expressed renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 20 mL / min) expressed by human liver, psoriasis, restrictive cardiomyopathy , congenital heart disease or heart valve defect with severe hemodynamic disturbances, heart failure with myocardial infarction within the last 3 months, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HO BL), a strict diet.
Dosage
10mg
Indications
– Arterial hypertension. – coronary heart disease: stable angina. – CHF.
Interaction with other drugs
On the efficacy and tolerability of the bisoprolol may affect concomitant use of other drugs. Such interaction may also occur in those cases when the two drugs are taken over a short period of time.
The doctor should be informed about the acceptance of other drugs, even if they are received without a doctor’s prescription (ie, non-prescription drugs).
Not recommended combinations
Treatment of chronic heart failure
Class I antiarrhythmics (e.g., quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin, flecainide, propafenone), while the use of bisoprolol can reduce AV conduction and the contractile ability of the heart.
All indications for use of the drug bisoprolol
Blockers “slow” calcium channel (BCCI) verapamil type and to a lesser extent, diltiazem, while the use of bisoprolol can lead to a decrease of myocardial contractility and AV conduction disturbance. In particular, intravenous administration of verapamil in patients receiving beta-blockers may cause severe hypotension and AV blockade. Centrally acting antihypertensive agents (clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine, rilmenidine) can lead to a decrease in heart rate and reducing cardiac output and vasodilation due to the reduction of the central sympathetic tone. Abrupt withdrawal, especially before the abolition of beta-blockers, may increase risk of “rebound” hypertension.
Combinations requiring special care
Treatment of hypertension and angina
Class I antiarrhythmic agents while the use of bisoprolol can reduce AV conduction and contractility of the myocardium.
All indications for use of the drug bisoprolol
BCCI dihydropyridine derivatives (e.g. nifedipine, felodipine, amlodipine) while the application of bisoprolol can increase the risk of hypotension. In patients with heart failure can not eliminate the risk of further deterioration of the contractile function of the heart.
Class III antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone) may enhance violation AV conduction.
The action of beta-blockers for topical (e.g., eye drops for treating glaucoma) may enhance the systemic effects of bisoprolol (decrease in blood pressure, heart rate reduction).
Parasympathomimetics while the use of bisoprolol can exacerbate violation of AV conduction and increase the risk of bradycardia.
Hypoglycemic effect of insulin or hypoglycemic agents for oral administration may be enhanced. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia – particularly tachycardia, may be masked or suppressed. Such interactions are more likely to occur when using non-selective beta-blockers.
Funds for general anesthesia may increase the risk cardiodepressive action, resulting in hypotension (see. Section “Special Instructions”).
Cardiac glycosides while the use of bisoprolol can lead to an increase of the pulse and thus to the development of bradycardia.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may reduce the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol.
The simultaneous use of bisoprolol formulation with beta-agonists (e.g., isoprenaline, dobutamine) may reduce the effect of both drugs.
Bisoprolol combination with agonists affecting the beta- and alpha-adrenergic receptors (such as norepinephrine, epinephrine) may enhance vasoconstrictor effects of these agents arising with alpha-adrenoceptors, leading to increased blood pressure. Such interactions are more likely to occur when using non-selective beta-blockers.
Antihypertensives, and other agents with antihypertensive effect (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazine) may enhance the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol.
Mefloquine while the use of bisoprolol may increase the risk of bradycardia.
Monoaminoskidazy inhibitors (MAO) except MAO B inhibitors may enhance the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers. Concomitant use can also lead to the development of hypertensive crisis.
Overdose
Symptoms: AV block, bradycardia, marked reduction in blood pressure, bronchospasm, acute cardiac insufficiency and hypoglycaemia.
Sensitivity to single high dose bisoprolol reception varies greatly among individual patients and probably patients with CHF have a high sensitivity.
Treatment: If overdose occurs, first of all, you need to stop taking the drug and start supporting symptomatically. – in severe bradycardia: intravenous administration of atropine. If the effect is insufficient, you can enter with caution agent with positive chronotropic effect. Sometimes it may require temporary staging pacemaker; – if marked decrease in blood pressure: intravenous plasma-substituting solutions and vasopressor drugs; – with AV blockade: patients should be under constant supervision and be treated with beta-agonists (epinephrine). If necessary – setting an artificial pacemaker; – during exacerbation flow CHF: intravenous diuretics, drugs with a positive inotropic effect, vasodilators; – with bronchospasm: the appointment of bronchodilators including beta2-agonists and / or aminophylline; – hypoglycemia: intravenous administration of dextrose (glucose).
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Selective beta1-blocker.
Pharmacodynamics:
Selective beta1-adrenergic blocker without own sympathomimetic activity, has no membrane stabilizing effect. It has negligible affinity for beta2 adrenoceptors bronchial smooth muscle and blood vessels, as well as the beta2-adrenoceptor involved in metabolic regulation. Hence, bisoprolol generally has no effect on airway resistance and metabolic processes that are involved in the beta2-adrenergic receptors.
The selective effect of the drug on beta1-adrenergic receptors is stored outside the therapeutic range.
Bisoprolol has no pronounced negative inotropic effect. The maximum effect of the drug is achieved within 3-4 hours after ingestion. When a single application bisoprolol effect lasts for 24 hours. The maximum decrease in blood pressure (BP) reached after 2 weeks of treatment.
Bisoprolol reduces the activity of sympatic system, blocking the beta1-adrenergic receptors of the heart.
When a single oral administration in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) without signs of congestive heart failure (CHF), bisoprolol reduces the heart rate (HR), cardiac stroke volume decreases and, as a consequence, ejection fraction and reduces myocardial oxygen demand. Prolonged therapy initially increased total peripheral vascular resistance (SVR) is reduced. Reducing the activity of renin in blood plasma is considered as one of the components of the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers.
Pharmacokinetics:
Selective beta1-adrenergic blocker without own sympathomimetic activity, has no membrane stabilizing effect. It has negligible affinity for beta2 adrenoceptors bronchial smooth muscle and blood vessels, as well as the beta2-adrenoceptor involved in metabolic regulation. Therefore, bisoprolol generally does not affect the airway resistance and metabolic processes that are involved in the beta2-adrenergic receptors.
The selective effect of the drug on beta1-adrenergic receptors is stored outside the therapeutic range.
Bisoprolol has no pronounced negative inotropic effect. The maximum effect of the drug is achieved within 3-4 hours after ingestion. When a single application bisoprolol effect lasts for 24 hours. The maximum decrease in blood pressure (BP) reached after 2 weeks of treatment.
Bisoprolol reduces the activity of sympatic system, blocking the beta1-adrenergic receptors of the heart.
When a single oral administration in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) without signs of congestive heart failure (CHF), bisoprolol reduces the heart rate (HR), cardiac stroke volume decreases and, as a consequence, ejection fraction and reduces myocardial oxygen demand. Prolonged therapy initially increased total peripheral vascular resistance (SVR) is reduced. Reducing the activity of renin in blood plasma is considered as one of the components of the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers.
Metabolism. Metabolized by oxidative way without subsequent conjugation. All metabolites are polar (water soluble) and excreted by the kidneys. The main metabolites found in blood plasma and urine, does not exhibit pharmacological activity. Bisoprolol is metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme in 95% and via CYP2D6 an enzyme which plays an insignificant role.
Withdrawal. About 50% of the drug is metabolized in the liver metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. 50% of bisoprolol is excreted by the kidneys unchanged. The total clearance is 15 l / h. The half – 10-12 hours.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
In pregnancy, the drug bisoprolol should be advised to use only if the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk of side effects in the fetus and / or the child.
Beta-blockers reduce blood flow to the placenta and can affect fetal development. It is necessary to monitor blood flow in the placenta and uterus, as well as to observe the growth and development of the unborn child and in case of occurrence of adverse events in relation to pregnancy and / or fetus, the use of alternative therapies.
It is necessary to carefully examine the newborn after delivery. In the first three days of life may have symptoms of hypoglycemia and bradycardia.
Information on the allocation of the breast milk is not present, so the drug bisoprolol is not recommended for women during breastfeeding. If administration during lactation is necessary, breast-feeding should be discontinued.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Available on medical prescription.
side effects
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) classified undesirable effects in accordance with the frequency of their development as follows: very often (more than or equal to 1/10), often (more than 1/100, less than 1/10) infrequently (more than 1/1000 , less than 1/100), rare (more than 1/10000, less than 1/1000), very rare (less than 1/10000, including isolated reports).
Central nervous system: often – headache * dizziness *, rare – loss of consciousness.
General disorders: often – asthenia (patients with chronic heart failure), fatigue *, not often – asthenia (patients with arterial hypertension or angina).
Psychiatric disorders: rarely – depression, insomnia, rarely – hallucinations, nightmares.
On the part of the organs of vision: rarely – reducing watery eyes (to consider when wearing contact lenses), very rarely – conjunctivitis.
On the part of the hearing organs: rarely – hearing impairment.
Cardio-vascular system: very often – bradycardia (in patients with heart failure), often – the aggravation of heart failure flow symptoms (in CHF patients), feeling cold weather or numbness in the extremities, marked reduction in blood pressure, especially in patients with CHF, infrequently – violation of AV conduction, bradycardia (in patients with arterial hypertension or angina pectoris), worsening of current symptoms of heart failure (in patients with hypertension and angina), orthostatic hypotension.
The respiratory system: rarely – bronchospasm in patients with asthma or airway obstruction in history, rarely – allergic rhinitis.
From the digestive system: often – nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, rarely – hepatitis.
On the part of the musculoskeletal system: rarely – muscle weakness, muscle cramps.
For the skin: rarely – hypersensitivity reactions (itching, skin rash, redness of the skin), very rare – alopecia; beta-blockers may exacerbate psoriasis symptoms or cause flow posriazopodobnuyu rash.
On the part of the reproductive system: rarely – a violation of potency.
Laboratory findings: rarely – increased concentration triglitselidov and “liver” trasaminaz blood (aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT)).
* In patients with hypertension or angina, these symptoms most often appear at the beginning of treatment. Usually, these effects are mild and are usually within 1-2 weeks after starting treatment.
special instructions
Should not abruptly discontinue treatment with bisoprolol or alter the recommended dosage without first consulting your doctor, as this may lead to temporary impairment of the heart. Treatment should not be interrupted suddenly, especially in patients with CAD. If discontinuation is necessary, the dose should be reduced gradually. In the initial stages of treatment with bisoprolol patients need constant supervision.
The drug should be used with caution in the following cases: – severe COPD and mild form of asthma; – diabetes with considerable fluctuations in blood glucose concentration: hypoglycemia symptoms such as tachycardia, palpitations or sweating, can be masked; – strict diet; – conducting desensitizing therapy; – AV I blockade degree; – Prinzmetal angina; – disorders of peripheral blood circulation mild and moderate (at the start of therapy may be increased symptoms); – psoriasis (including history);
Respiratory system: bronchial asthma or COPD shown the simultaneous application of bronchodilatory agents. Patients with asthma may increase airway resistance that require high doses of beta2-agonists. In patients with COPD, bisoprolol, appointed in the complex therapy for the treatment of chronic heart failure, you should start with the lowest possible dose, and the patient carefully monitored and tracked new symptoms (such as shortness of breath, exercise intolerance, cough).
Allergic reactions: beta blockers, including drug bisoprolol, may increase the sensitivity to allergens and severity of anaphylactic reactions due to weakening adrenergic compensatory regulation under their action. Therapy with epinephrine (adrenaline) does not always give the expected therapeutic effect.
General anesthesia: general anesthesia should be taken into account the risk of beta-blockade adrenoreptorov. If you want to stop therapy with bisoprolol before surgery, this should be done gradually and completed within 48 hours before the general anesthetic. Следует предупредить врача-анестезиолога о том, что вы принимаете препарат Бисопролол.
Феохромоцитома: у пациентов с опухолью надпочечников (феохромоцитомой) препарат Бисопролол может быть назначен только на фоне применения альфа-адреноблокаторов.
Гипертиреоз: при лечении препаратом Бисопролол симптомы гиперфункции щитовидной железы (гипертиреоза) могут маскироваться.
Effects on ability to drive vehicles and management mechanisms
Препарат Бисопролол не влияет на способность управлять автотранспортом согласно результатам исследования у пациентов с ИБС. Однако вследствие индивидуальных реакций способность управлять автотранспортом или работать с технически сложными механизмами может быть нарушена. На это стоит обратить особое внимание в начале лечения, после изменения дозы, а также при одновременном употреблении алкоголя.
Storage conditions
In a dry, dark place at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Препарат Бисопролол следует принимать один раз в сутки с небольшим количеством жидкости, утром до завтрака или после него. Таблетки не следует разжевывать и растирать в порошок
Артериальная гипертензия и стабильная стенокардия
Во всех случаях режим приема и дозу подбирает врач каждому пациенту индивидуально, в частности, учитывая ЧСС и состояние пациента.
Обычно начальная доза составляет 5 мг препарата Бисопролол 1 раз в день. При необходимости дозу можно увеличить до 10 мг 1 раз в сутки.
Рекомендованная максимальная доза составляет 20 мг препарата Бисопролол 1 раз в день.
Chronic heart failure
Бета-адреноблокаторы наряду с другими гипотензивными и диуретическими препаратами входит в стандартную схему лечения ХСН. Start treating heart failure drug bisoprolol requires a mandatory holding a special titration phase and regular medical supervision.
Предварительным условием для лечения препаратом Бисопролол является стабильная ХСН без признаков обострения.
Лечение ХСН препаратом Бисопролол начинается в соответствии со схемой титрования. This may require individual adaptation depending on how well patients tolerate the prescribed dose, t. E. The dose can be increased only if the previous dose was well tolerated.
Для обеспечения соответствующего процесса титрования на начальных этапах лечения рекомендуется применять бисопролол в лекарственной форме: таблетки по 2,5 мг. Рекомендуемая начальная доза составляет 1,25 мг один раз в день. В зависимости от индивидуальной переносимости дозу следует постепенно повышать до 2,5 мг, 3,75 мг, 5 мг, 7,5 мг и 10 мг 1 раз в день. Each subsequent increase in dose should be administered at least two weeks.
If an increase in the dose of the drug is poorly tolerated by the patient, may reduce the dose.
Рекомендованная максимальная доза при лечении ХСН составляет 10 мг препарата Бисопролол 1 раз в день.
During titration we recommend regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and severity of heart failure symptoms. Усугубление симптомов течении ХСН возможно уже с первого дня применения препарата.
Если пациент плохо переносит рекомендованную максимальную дозу препарата, следует рассмотреть возможность постепенного снижения дозы.
Во время фазы титрования или после нее могут возникать временное ухудшение течения ХСН, артериальная гипотензия или брадикардия. In this case it is recommended first of all to carry out correction of drug doses of concomitant therapy. Так же может потребоваться временное снижение дозы препарата Бисопролол или его отмена.
After stabilization of the patient should be a re-titration of the dosage or further treatment.
Продолжительность лечения при всех показаниях к применению препарата Бисопролол
Лечение препаратом Бисопролол обычно является долговременной терапией.
Special patient groups
Нарушение функции почек или печени – При нарушении функции печени или почек легкой или умеренной степени обычно не требуется корректировать дозу. – При выраженных нарушениях функции почек (КК менее 20 мл/мин) и у пациентов с тяжелыми заболеваниями максимальная суточная доза составляет 10 мг. Увеличение дозы у таких пациентов должно осуществляться с особой осторожностью.
Пожилые пациенты -коррекции дозы не требуется.
Дети – так как нет достаточного количества данных по применению препарата Бисопролол у детей, не рекомендуется назначать препарат детям до 18 лет.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SYNTHESIS |












There are no reviews yet.