- No products in the cart.
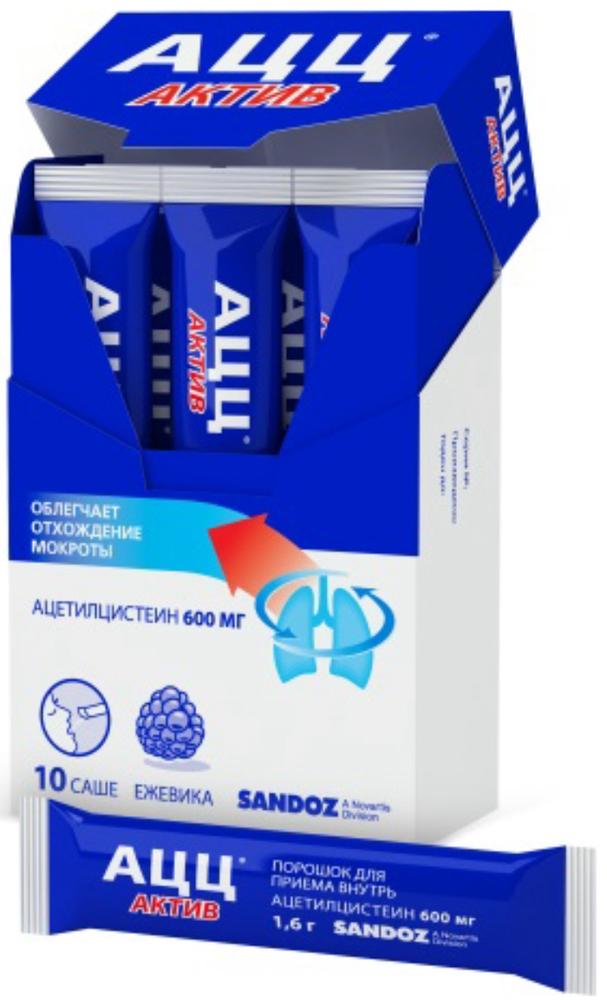
ACC asset powder vn.pr. 600mg sachet 10 pc
$12.38
ACC asset powder vn.pr. 600mg sachet 10 pc
Description
Composition
Active substance:
Stick 1 comprises: 600 mg acetylcysteine
Excipients:
glyceryl tripalmitate, polysorbate 65, corbitol, xylitol, citric acid, sodium citrate, magnesium citrate, sodium carmellose, aspartame, flavoring Blackberry “B” (natural / nature-identical liquid flavor “Forest berry”, code 5752; natural / nature-identical liquid flavor ” blackBerry “, code 5337; vanillin; maltodextrin, mannitol, gluconolactone, sorbitol, colloidal anhydrous silica, magnesium carbonate), magnesium stearate.
Description:
The powder is white to yellowish-white in color with easy-disintegrating agglomerates, with the smell of blackberries. Perhaps the presence of a weak sulfur smell.
Product form:
Powder for oral administration of 600 mg
For 1.6 g of powder was placed in a sachet made of paper laminated with aluminum foil.
10 or 20 sachets together with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine or other components of the formulation;
Hemoptysis, pulmonary hemorrhage;
Gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer in the acute stage;
Children under the age of 18 years (the dosage form);
Pregnancy and lactation;
Hereditary fructose intolerance (containing sorbitol), phenylketonuria (phenylalanine source comprises aspartame).
Carefully.
Gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer history, bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis, liver and / or kidney failure, intolerance to histamine (avoid prolonged use, since acetylcysteine has an effect on the metabolism of histamine, which can lead to symptoms intolerant, such as headache, vasomotor rhinitis, itching), varicose veins of the esophagus, adrenal disease, hypertension.
Dosage
600 mg
Indications
Acute and chronic respiratory disease associated with the formation of a viscous trudnootdelyaemogo bronchial secretion (as an expectorant): bronchitis, tracheitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, lung abscess, pulmonary emphysema, laryngotracheitis, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary atelectasis (due blockage of the bronchi of the mucous plug).
Inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media), acute and chronic sinusitis, rhinosinusitis (facilitating discharge of secretion).
Removal of viscous secretions from the airways in post-traumatic and postoperative states.
Interaction with other drugs
With simultaneous use of acetylcysteine with antitussive drugs for suppressing the cough reflex can occur sputum bronchial congestion. Before the appointment of such combination therapy require careful assessment of the patient’s condition.
Evidence to date reports acetylcysteine inactivation of antimicrobials such as tetracyclines (except doxycycline), aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, penicillins (ampicillin), and antifungal drugs (amphotericin B) relate exclusively to studies in vitro (pharmaceutical incompatibility). Nevertheless, antibacterial agents for oral administration and a preparation ATSTS® asset should be applied at intervals of not less than 2 hours (not applicable to loracarbef and cefixime).
The simultaneous use of acetylcysteine can lead to increased vasodilator and antiplatelet effects of nitroglycerin. If you want to share the use of nitroglycerin and acetylcysteine, it is necessary to monitor the patient for potential development of arterial hypotension (sometimes severe, may appear headache).
The simultaneous use of acetylcysteine and carbamazepine can be expressed in reducing the concentration of carbamazepine to subtherapeutic levels.
The simultaneous use of activated carbon can reduce the effect of acetylcysteine.
Acetylcysteine eliminates the toxic effects of paracetamol.
Overdose
Cases toxic overdoses while taking into acetylcysteine not described. Acetylcysteine when taken in doses up to 500 mg / kg / day did not cause symptoms of overdose. Healthy volunteers received a dose acetylcysteine 11.6 g per day for 3 months without developing any severe adverse reactions.
Symptoms may occur such gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy if necessary.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Mucolytic expectorant.
Pharmacodynamics:
Acetylcysteine is a derivative of the amino acid cysteine. Has mucolytic and secretomotoric effects in the respiratory tract, facilitates expectoration due to the direct impact on the rheological properties of sputum. The action of the drug due to its ability to break free sulfhydryl groups of intra- and intermolecular disulfide bonds, acid mucopolysaccharides mucus, which leads to depolymerisation mukoproteidov and decrease sputum viscosity.
Furthermore, reduces induced hyperplasia mucoid cells increases the production of surface-active compounds (surfactant) by stimulation of type II pneumocytes, it stimulates ciliary activity, which leads to improvement of mucociliary clearance.
The drug remains active in the presence of purulent, muco-purulent sputum and mucous.
Increases secretion less viscous sialomutsinov goblet cells, reduces the adhesion of bacteria to the epithelial cells of the bronchial mucosa. Stimulates bronchial mucosa cells, the secret of which lyses fibrin.
A similar effect on the secretion produced in inflammatory diseases of upper respiratory tract.
It has an antioxidant effect, due to the presence of sulfhydryl groups (SH-groups) able to neutralize electrophilic toxins oxidation. Acetylcysteine easily penetrates into cells, where deacetylated to L-cysteine, which is synthesized from the intracellular glutathione. Glutathione – highly reactive tripeptide powerful antioxidant cytoprotector, trapping endogenous and exogenous toxins and free radicals. Acetylcysteine prevents depletion and contributes to intracellular glutathione synthesis involved in redox processes in cells, thus contributing to detoxification of harmful substances. This explains the effect of acetylcysteine as an antidote for poisoning by paracetamol. Paracetamol exerts its cytotoxic effect through a progressive depletion of glutathione. Acetylcysteine primary role is to maintain an adequate level of glutathione concentration that provides protection for the cells.
Protects the alpha-1-antitrypsin (elastase inhibitor) of the inactivating action of HOCl – oxidant active myeloperoxidase produced by phagocytes. Also has anti-inflammatory action (by inhibiting the formation of free radicals and active oxygen-containing compounds are responsible for the development of inflammation in lung tissue).
When prophylactic use acetylcysteine marked reduction in the frequency and severity of exacerbations of bacterial infections in patients with chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis.
Pharmacokinetics:
Suction
Acetylcysteine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed by ingestion. Due to the high first-pass metabolism (the effect of “first pass” through the liver), oral bioavailability forms acetylcysteine is about 10%. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in plasma acetylcysteine after ingestion achieved after 1-3 hours and is 15 mmol / l, Cmax metabolite of cysteine is about 2 mol / l.
Distribution
Communication with the plasma proteins is approximately 50% at 4 hours and decreases to 20% after 12 hours.
Acetylcysteine is distributed both in unchanged form (20%), as well as active metabolites (80%), penetrates into the extracellular space, is distributed predominantly in the liver, kidney, lung and bronchial secretions. Acetylcysteine crosses the placenta and umbilical cord blood is determined. Information on excretion in breast milk is not available. Data on acetylcysteine ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier is absent.
Metabolism
Acetylcysteine is metabolized in the liver to cysteine - a pharmacologically active metabolite, as well as to diatsetiltsisteina, cystine and other mixed disulfides. In the body acetylcysteine and its metabolites can be detected in a variety of forms: a free form, bound to plasma proteins labile disulfide bonds or linked amino acids.
breeding
Acetylcysteine is recovered almost exclusively in the form of inactive metabolites (inorganic sulfates diatsetiltsisteina) kidneys, a small part is released unchanged through the gut. Period (T1 / 2) half-life of the drug from the blood plasma of about 1 hour, depending on the rate of biotransformation in the liver. In human liver T1 / 2 acetylcysteine can be increased to 8 hours.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Pregnancy. Experimental studies in animals have not shown direct or indirect harmful effects of the drug on pregnancy, embryonic / fetal development, birth or postnatal development of the fetus. Clinical data for use during pregnancy acetylcysteine limited, so the use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated.
If necessary, use during lactation should stop breastfeeding.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Without recipe.
side effects
Violations by the immune system.
infrequently: hypersensitivity reactions;
very rare: anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic / anaphylactoid reactions.
Disorders of the nervous system.
Uncommon: headache.
Violations of the heart and blood vessels.
Uncommon: tachycardia, hypotension;
very rarely: bleeding;
frequency is unknown: when receiving acetylcysteine cases of collapse described.
Violations of the respiratory system.
rare: dyspnea, bronchospasm (predominantly in patients with bronchial hyperresponsiveness in the background of asthma).
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Uncommon: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis;
rare: indigestion;
Frequency not known: heartburn.
Violations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Uncommon: urticaria, rash, rash, angioedema, pruritus;
very rare: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell’s syndrome (see section “Special Instructions”.).
Violations by the organ of hearing and labyrinth disorders.
Uncommon: tinnitus.
Common disorders.
rare: fever;
frequency is unknown: swelling of the face.
special instructions
Patients with bronchial asthma and obstructive bronchitis acetylcysteine should be used with caution under systematic control of bronchial obstruction. If the patient is unable to cough effectively, it is necessary to carry out drainage or aspiration of secretions.
In applying acetylcysteine rarely reported cases of severe allergic reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell syndrome. In the event of changes in the skin and mucous membranes should immediately consult a doctor, the drug should be discontinued.
It should not take the drug just before bedtime (it is recommended to take the drug to 18.00).
Effect on laboratory data. Acetylcysteine may affect the results of the colorimetric determination of salicylate concentration in blood plasma. In the analysis of urine acetylcysteine may affect the results of the determination of ketone bodies.
Effects on ability to drive vehicles, machinery.
Acetylcysteine does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
Storage conditions
Stored in original package at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Inside. 1 sachet of powder to be poured directly into the language. The drug stimulates the secretion of saliva, so the powder is mixed with saliva and swallowed easily. The drug does not require zapivaniya water. Powder for oral administration should not be chewed before swallowing.
Adults: 1 sachet once daily (equivalent to 600 mg of acetylcysteine in the night).
Due to the high content acetylcysteine (600 mg) in 1 Sachet formulation should not be used in children (recommended ATSTS® other dosage forms of the drug or another drug acetylcysteine).
The duration of treatment should be evaluated individually. At brief colds course duration is 5-7 days, in the treatment of chronic diseases – up to several months (on doctor’s advice).
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Sandoz UTS |








There are no reviews yet.