- No products in the cart.
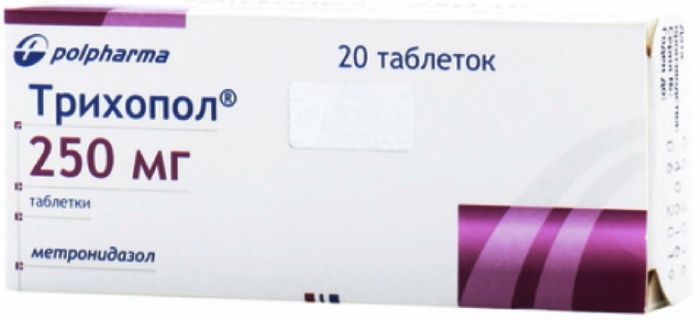
Trihopol 250mg 20 pieces Table
$2.33
Trihopol 250mg 20 pieces Table
SKU: 234116090 Categories: Antibiotics, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, Antiprotozoal, Medicaments Tag: QUINACRINE INN
Description
Composition
Active substance:
1 tablet contains 250 mg of metronidazole.
Excipients:
Potato starch, gelatin, molasses, starch, magnesium stearate.
Description:
Round Valium pills white with a yellowish tint; with bevel on both sides and on one side of the notch. Tablets yellow when exposed to light.
Product form:
Tablets of 250 mg. 10 tablets in a blister made of PVC / Al foil.
2 blisters together with instructions for use placed in a cardboard box.
Contraindications
• Increased sensitivity to metronidazole and other nitroimidazole derivatives, as well as any other ingredients of the formulation; • leukopenia (including in history); • Organic lesions of the central nervous system (including epilepsy); • liver failure (in the case the destination of large doses of the drug); • pregnancy (I term); • lactation; • Children under 3 years of age (for a given dosage form).
Precautions: Pregnancy (II-III trimesters), renal / hepatic failure.
Dosage
250 mg
Indications
• Trichomoniasis; • Bacterial Vaginosis; • all forms amebiasis (intestinal and extraintestinal disorders localization, including amebic liver abscess, amoebic dysentery and asymptomatic amoebiasis); • giardiasis; • periodontal infections (including, acute ulcerative gingivitis, acute odontogenic infection); • anaerobic bacterial infections (gynecological and abdominal infections, central nervous system infections, bacteremia, sepsis, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, skin and soft tissue, respiratory tract infection), caused by Bacteroides spp., Clostridium spp., Eubacterium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp. and other anaerobes sensitive to metronidazole. • Helicobacter pylori infection during peptic ulcer treatment 12 duodenum or stomach in combination with bismuth preparations and antibiotics, such as amoxicillin. • Prophylactic before surgery on the gastrointestinal tract and reproductive organs.
Interaction with other drugs
Metronidazole potentiates the effect of warfarin and other coumarin anticoagulants, however, while the appointment doses of these drugs should be reduced. Similarly, disulfiram is intolerant of ethanol. The simultaneous use of disulfiram can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms (interval between administration – at least 2 weeks).
Cimetidine inhibits metabolism of metronidazole, which may lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood serum and the risk of an increase of side effects.
Simultaneous administration of drugs that stimulate the microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver (phenobarbital, phenytoin), may accelerate the elimination of metronidazole, resulting in decreases its concentration in plasma.
In patients receiving long-term lithium treatment with drugs in high doses, when taking metronidazole may increase the concentration of lithium in blood plasma and the development of symptoms of intoxication.
Metronidazole is not recommended to combine with non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (vecuronium bromide).
In the combined receiving cyclosporine and metronidazole may experience increased concentration of cyclosporine in the blood plasma.
Metronidazole reduces the clearance of fluorouracil, which may cause an increase in the toxicity of the latter.
Sulfonamides enhance the antimicrobial activity of metronidazole.
Overdose
The lethal dose for humans is unknown. Excessive doses can cause amplification of side effects, mainly nausea, vomiting, and vertigo; In more severe cases, there may be a ataxia, paresthesias, and seizures.
In the case of poisoning apply symptomatic and supportive treatment. There is no specific antidote.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Antiprotozoal drug with antibacterial activity.
Pharmacodynamics:
Metronidazole is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole derivatives with antiprotozoal and antibacterial action. The mechanism of action is in the biochemical reduction of 5-nitro intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The recovered 5-nitro interacts with DNA microbial cells by inhibiting synthesis of nucleic acids, which leads to the death of the bacteria.
Metronidazole is active against: Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytisa, Gardnerella vaginalis, Giardia intestinalis, Lamblia spp, and obligate anaerobes Bacteroides spp.. (Including, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus), Fusobacterium spp., Veillonella spp., Prevotella (Prevotella bivia, Prevotella buccae, Prevotella disiens) and some Gram-positive organisms (Eubacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for these strains is 0,125-6,25 mg / ml.
In combination with amoxicillin is active against Helicobacter pylori (amoxicillin suppresses development of resistance to metronidazole).
Metronidazole has no bactericidal action against most aerobic bacteria and facultative anaerobes, fungi and viruses. In the presence of mixed flora (aerobes and anaerobes) metronidazole acts synergistically with antibiotics effective against common aerobes.
Increases of tumor sensitivity to radiation, causes sensitization to alcohol (disulfiramopodobnyh action), stimulates repair processes.
Pharmacokinetics:
Metronidazole is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the digestive tract, bioavailability of not less than 80%. The presence of food decreases the rate of absorption and the maximum concentration of metronidazole in serum. Less than 20% of the drug binds to serum proteins.
Metronidazole penetrates into most tissues and body fluids, including the lungs, kidneys, liver, skin, spinal fluid, brain, bile, saliva, amniotic fluid, oral abscesses, vaginal secretions, semen, breast milk, penetrates the blood-brain and placental barrier . The volume of distribution in adults is about 0.55 l / kg, neonatal – 0.54 – 0.81 L / kg.
The maximum concentration of metronidazole in the blood is achieved in 1-3 hours.
About 30 – 60% metronidazole metabolized by hydroxylation, oxidation and reaction with glucuronic acid. The main metabolite of metronidazole (2-oximetronidazole) also exhibits antibacterial action and protivoprotozoynoe.
The half-life (T1 / 2) for normal liver function is an average of 8 hours (6 to 12 hours); in alcoholic liver disease – 18 h (from 10 to 29 hours); in infants born at a gestational age 28 – 30 weeks – about 75 hours; 32 – 35 weeks – 35 h, 36 – 40 weeks – 25 hours, respectively.
Metronidazole and major metabolites are rapidly removed from the blood by hemodialysis (T1 / 2 is reduced to 2.6 hours). When peritoneal dialysis is output in minor amounts.
Excreted by the kidneys 60 – 80% of metronidazole (20% unchanged) through the intestine – 6 – 15% of the applied dose. The renal clearance of the drug is 10.2 ml / min. Patients with impaired renal function after repeated administration cumulation of metronidazole in serum can be observed (hence patients with severe renal impairment receiving frequency to be reduced).
Renal excretion of metronidazole is reduced in elderly patients.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Metronidazole crosses the placenta and should not be prescribed the drug in the first trimester of pregnancy, in the future should only be used if the potential benefits of the drug to the mother than the potential risk to the fetus.
Because Metronidazole passes into breast milk, reaching concentrations it close concentration in the blood plasma, it is recommended to stop breast-feeding during treatment with the drug.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
On prescription.
side effects
On the part of the gastrointestinal tract: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, intestinal colic, loss of appetite, anorexia, taste disturbance, unpleasant “metallic” taste in the mouth, dry mouth, glossitis, stomatitis; very rarely – a deviation from the norm of the test results on liver function, cholestatic hepatitis, jaundice, pancreatitis.
On the part of the central nervous system: long-term use – headache, dizziness, incoordination, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, nervousness, irritability, depression, sleep disturbance, drowsiness, weakness; in some cases – confusion, hallucinations, convulsions; very rarely – encephalopathy.
With the genitourinary system: dysuria, cystitis, polyuria, urinary incontinence, candidiasis, pain in the vagina, urine staining in red-brown color.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, pruritus, urticaria, erythema multiforme exudative, nasal congestion, fever.
On the part of the musculoskeletal system: myalgia, arthralgia.
On the part of the hematopoietic system: leukopenia; rarely – agranulocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia.
Miscellaneous: flattening of the T wave on an electrocardiogram; rarely – ototoxicity; pustular rash.
special instructions
Patients with severe hepatic insufficiency Metronidazole should be used with caution, as a result of slow metabolism concentration of metronidazole and its metabolites in plasma increases.
Due to the slow excretion need to be careful when choosing the dose of metronidazole in patients with renal insufficiency. In such patients, the dose should be reduced by half.
Metronidazole should be used with extreme caution in patients with bone marrow depression and central nervous system, as well as in elderly patients. The emergence of ataxia, dizziness and any other worsening of neurological status of patients required discontinuation of treatment.
When long-term therapy with metronidazole (over 10 days) should be monitored picture peripheral blood and liver function.
When leukopenia possibility of further treatment depends on the risk of infection.
In combination with amoxicillin did not use the drug in patients younger than 18 years.
Avoid the use of metronidazole in patients with porphyria.
Can immobilize treponema and lead to false positive test Nelson.
In the treatment of Trichomonas vaginitis in women and urethritis in men Trichomonas should refrain from sexual activity. Required simultaneous treatment of sexual partners. After treatment of trichomoniasis should hold control samples for three consecutive cycles before and after menstruation.
After treatment of giardiasis, if symptoms persist after 3 – 4 weeks is necessary to conduct the analysis of stool 3 at intervals of a few days (some successfully treated cases of lactose intolerance, caused by the invasion, may persist for several weeks or months, reminding giardiasis symptoms).
Patients should abstain from alcohol during treatment with metronidazole and for at least 48 hours after completion of treatment, due to the possibility of disulfiramopodobnyh reactions: abdominal pain, spastic nature, nausea, vomiting, headache, a sudden rush of blood to face.
During treatment with metronidazole urine may be dark or reddish-brown color due to the presence of water-soluble dyes.
Effect on driving performance and requiring a high rate of mental and physical reactions
When potentially hazardous should avoid taking the drug activities that require attention, rapid mental and motor responses, especially driving vehicles and servicing arrangements.
Storage conditions
In the dark place at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Inside, during or after a meal, without chewing.
trichomoniasis
Adults and children over 10 years:
250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times daily or 500 mg (2 tablets), 2 times a day for 7 days. Women must additionally assign metronidazole in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets. you can repeat the treatment if necessary. should make a break between courses in 3 – 4 weeks to conduct repeated control laboratory tests.
An alternative scheme is to assign therapy 750 mg (3 tablets) in the morning and 1,250 mg (5 tablets) or evening 2000 mg (8 tablets) as a single daily dose. The treatment duration is 2 days.
Treatment is carried out simultaneously in both sexual partners.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablet), 2 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablets) 3 times a day.
The course of treatment was 7 days.
bacterial vaginosis
Adults:
500 mg (2 tablets), 2 times a day for 7 days, or 2000 mg (8 tablets) in a single dose.
Simultaneous treatment of sexual partners is not required.
amoebiasis
Invasive amebiasis intestinal forms in susceptible patients (including amoebic dysentery)
Adults and children over 10 years:
750 mg (3 tablets) 3 times a day.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 250 mg (1 tablet) 4 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 375 mg (1.5 tablets) 3 times a day.
The treatment is usually 5 days.
intestinal amebiasis have less susceptible patients and in chronic amoebic hepatitis
Adults and children over 10 years:
375 mg (1.5 tablets) 3 times a day.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablets) 4 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
The duration of treatment is 5 – 10 days.
Amebic liver abscess and other forms of extraintestinal amebiasis
Adults and children over 10 years:
375 mg (1.5 tablets) 3 times a day.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablets) 4 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
The course of treatment was 5 days.
Asymptomatic carriage of cysts
Adults and children over 10 years:
375 – 750 mg (1.5 – 3 tablets) 3 times a day.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablets) 4 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
The duration of treatment is 5 – 10 days.
giardiasis
Adults and children over 10 years:
500 mg (2 tablets), 2 times a day for 5 days -7; or
To 2000 mg (8 tablets) 1 times a day for 3 days.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 250 – 375 mg (1 – 1.5 tablets) 1 times a day for 5 days or 500 – 750 mg of (2 – 3 tablets) 1 time per day for 3 days; from 7 to 10 years – 250 mg (1 tablet), 2 times a day for 5 days, or 1000 mg (4 tablets) 1 time per day for 3 days.
periodontal infection
Acute ulcerative gingivitis
Adults and children over 10 years:
250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
Children: from 3 to 7 years – 125 mg (1/2 tablet), 2 times a day; from 7 to 10 years – 125 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
The duration of treatment is 3 days.
Acute odontogenic infection
Adults and children over 10 years:
250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day for 3 – 7 days.
Infections caused by anaerobic bacteria
Treatment of anaerobic infections usually start with an intravenous infusion. As soon as this is possible, treatment should be continued tablets.
Adults and children over 10 years: 500 mg (2 tablets) 3 – 4 times daily.
Children under 10 years in the treatment of anaerobic infections we recommend the use of infusion solutions of metronidazole.
The duration of treatment should not exceed 7 days.
Helicobacter pylori eradication
500 mg (2 tablets) 3 times daily for 7 days (in a combination therapy, for instance, with amoxicillin 2.25 g per day).
Prophylaxis of infections caused by anaerobic bacteria (before surgery to the abdomen, in gynecology and obstetrics)
Adults and children over 12 years:
250 – 500 mg (1 – 2 tablets) 3 times a day for 3 – 4 days before surgery.
After 1 – 2 days after operation (when it is allowed to ingestion) 250 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day for 7 days.
When expressed renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 mL / min) of metronidazole daily dose should be reduced by 2 times.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | QUINACRINE INN |










There are no reviews yet.