- No products in the cart.
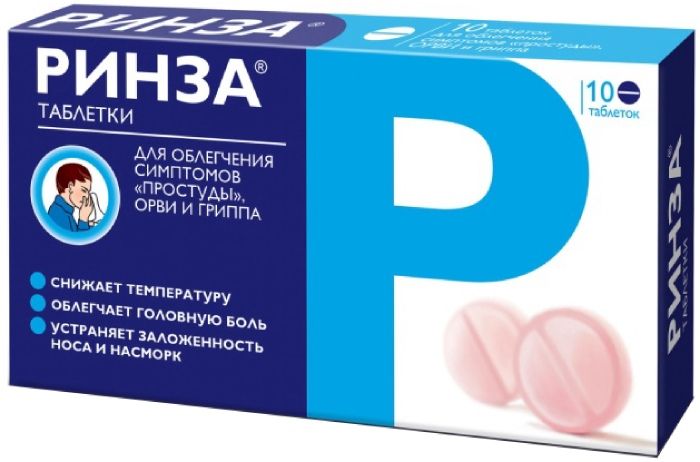
Rinzai 10 pcs Table

Nurofen for children oral suspension 100mg / 5ml 150ml vial with a syringe dosing orange
$4.17

Rinzasip powder for r-ra 5g 5 pcs black currants / Vitamin C.
$3.86
$3.50
Rinzai 10 pcs Table
SKU: 624575677 Categories: Cold and flu, Medicaments, Temperature Tags: paracetamol + caffeine + phenylephrine + chlorphenamine, Rinzai
Description
Composition
Active substance:
1 tablet contains: Caffeine – 30 mg paracetamol – 500 mg, phenylephrine hydrochloride -10 mg, chlorphenamine maleate – 2 mg.
Excipients:
Colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, corn starch (20% for paste), povidone (K30), sodium methyl parahydroxybenzoate, magnesium stearate, talc, sodium carboxymethylstarch (type A), a dye Ponceau [Ponceau 4R].
Description:
Round flat tablets of pink color with dark pink and white patches, with beveled edges and break line on one side.
Product form:
Tablets. 10 tablets in blister AL / AL or blister AL / PVC. 1 or 2 of the blister (10 or 20 tablets), together with instructions for use in a cardboard box.
Contraindications
Expressed atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries; arterial hypertension; portal hypertension; diabetes; concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO), beta-blockers; Hypersensitivity to paracetamol and other components forming part of the formulation; other medications containing substances included in the formulation Rinza®; pregnancy, lactation; children’s age (15 years); alcoholism.
Carefully
In hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hemolytic anemia, blood diseases, acute hepatitis, congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert syndrome, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor), hepatic and / or renal failure, simultaneous administration of drugs which could adversely affect on the liver (barbiturates, phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, rifampicin, isoniazid, zidovudine and other inducers of microsomal x fermantov liver) piloroduodenalnoy obstruction, stenosing gastric and / or duodenal ulcers, form-closure glaucoma, epilepsy, benign prostatic hyperplasia, as well as persons with deficiency of calories consumed with food Rinza® preparation can be used with caution after consultation with the physician.
Indications
Symptomatic treatment “colds”, SARS, including influenza (febrile syndrome, pain, rhinorrhea).
Interaction with other drugs
Enhances the effects of inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (MAO), sedatives, ethanol.
Antidepressants, antiparkinsonian agents, antipsychotics, phenothiazine derivatives – increase the risk of urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation. Corticosteroids increase the risk of developing glaucoma. Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. Metoclopramide and domperidone to increase, and cholestyramine reduces the rate of absorption of paracetamol. Paracetamol reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs. When concomitant administration with barbiturates, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampicin, isoniazid, zidovudine, and other inducers of microsomal liver enzymes, increased risk of hepatotoxic action of paracetamol. When the joint application of paracetamol and chloramphenicol chloramphenicol half-life can be increased. The majority of patients receiving long-term warfarin, occasional use of paracetamol is usually little or no effect on the international normalized ratio (INR). However, with continued regular use paracetamol enhances the effect of anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarin derivatives), which increases the risk of bleeding. Single administration of high doses of caffeine increases the lithium excretion by the kidneys. Abrupt cessation of caffeine may increase the concentration of lithium in blood serum.
Chlorphenamine simultaneously with inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (MAO), furazolidone may lead to hypertensive crisis, excitation of hyperpyrexia.
Concomitant use of phenylephrine with digoxin and other cardiac glycosides may increase the risk of arrhythmias and myocardial infarction.
Phenylephrine when taken with MAO inhibitors may lead to increased blood pressure. Phenylephrine reduces the effectiveness of beta-blockers and action of antihypertensive drugs.
Tricyclic antidepressants increase adrenomimeticheskoe effects of phenylephrine, co-administration of halothane increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. Decreases guanetidina hypotensive effect, which in turn enhances the activity of alpha-Adrenomimeticalkie phenylephrine.
Overdose
In case of overdose, you should immediately consult a doctor. Rapid medical assistance is critical, even if you do not see any signs or symptoms.
Caffeine
Symptoms of acute overdose: abdominal pain, vomiting, flushing, fever, chills, agitation, insomnia, irritability, loss of appetite, weakness, tremors, increased muscle tone, a state of altered consciousness, delirium, hallucinations, high blood pressure followed by hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, increased diuresis, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, convulsions, myoclonus, and rhabdomyolysis, supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias.
Symptoms of chronic intoxication, caffeine “caffeinism”: irritability, insomnia, anxiety, emotional lability, and chronic abdominal pain.
chlorphenamine
Symptoms: CNS depression, hyperthermia, anticholinergic syndrome (mydriasis, flushing, fever, dry mouth, urinary retention, intestinal paresis), tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, excitement, confusion, hallucinations, psychosis, seizures, arrhythmias . Rarely, patients with agitation, seizures or coma patients in developing rhabdomyolysis and renal failure.
phenylephrine
Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, irritability, agitation, insomnia, psychosis, convulsions, palpitations, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, reflex bradycardia.
Paracetamol
Symptoms appear after receiving more than 7.5 – 10 g: during the first 24 hours after administration – paleness of the skin, nausea, vomiting; anorexia, abdominal pain; increase in prothrombin time, impaired glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis (including lactic acidosis). Symptoms of liver disease may occur after 12 – 48 hours after the overdose: increased activity “liver” enzymes, gepatonekroz. In severe cases, – hepatic failure with progressive encephalopathy, coma. Rarely hepatic insufficiency develops lightning and can be complicated by renal insufficiency (tubular necrosis).
overdose threshold may be reduced in elderly patients and children, patients taking certain medications (e.g., inducers of hepatic microsomal enzymes), alcohol or malnourished.
Treatment: gastric lavage, appointment of activated carbon in the first 6 hours after the overdose, administration donators SH-groups and precursors of glutathione synthesis – methionine after 8 – 9 hours after the overdose and acetylcysteine after 12 hours The need for additional therapeutic activities (further administration of methionine. acetylcysteine) determined paracetamol concentration in the blood, and the time elapsed after administration. Symptomatic therapy.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Means for removing the symptoms of acute respiratory disease and “cold” (psychostimulant agent + non-narcotic analgesic agent adrenoagonists + alpha + H1 – histamine receptor blocker).
Pharmacological properties:
Combined preparation. Paracetamol has antipyretic and analgesic effect: it reduces pain syndrome, observed at cold conditions – sore throat, headache, muscle and joint pain, reduces high temperature. Phenylephrine has a vasoconstrictive action – reduces edema and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and sinuses. Chlorphenamine having antiallergic action: it removes itching eyes, nose and throat, swelling and congestion of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and sinuses, reduces exudative manifestations. Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system that leads to a decrease of fatigue and sleepiness to improve mental and physical performance.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
In the absence of clinical data, safety of the drug during pregnancy and lactation has not been established, therefore, use of the drug in this category of patients is contraindicated.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Without recipe.
side effects
Allergic reactions: skin rash, pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, sleep, irritability.
Cardio-vascular system: increased blood pressure, tachycardia, palpitations.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea, dryness of the oral mucosa, hepatotoxicity.
From the senses: mydriasis, accommodation paresis, it increased intraocular pressure.
From the side of blood: anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, methemoglobinemia, pancytopenia, leukopenia.
From the urinary system: renal toxicity (renal colic, Glycosuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), difficulty urinating.
Other: bronchospasm.
Serious skin reactions:
Very rare: – Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (OGEP). Acute conditions with the development of pustular rash. Characterized by fever and diffuse erythema, accompanied by burning and itching. There may be a swelling of the face, hands and mucous membranes;
– Stevens – Johnson (SSD) (malignant exudative erythema). Severe erythema multiforme form in which the bubbles emerge on the oral mucosa, throat, eyes, genital and other areas of skin and mucous membranes.
– Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN, Lyell syndrome). Syndrome is the result of extensive apoptosis of keratinocytes, which leads to the detachment of large areas of skin in places dermoepidermalnogo connection. Affected skin looks scalded with boiling water.
If you notice one of the above side effects, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately !.
special instructions
The treatment should abstain from alcohol, hypnotics and anxiolytics (tranquilizers) drugs. Do not take with other medicines containing paracetamol.
If symptoms worsen or persist after 5 days of the drug should stop taking it and consult a physician.
The drug can cause drowsiness.
If the drug has come into disrepair or expiration date – do not throw it in the sewer system or into the street! Place the drug in the bag and place in the trash. These measures will help protect the environment!
The drug can cause drowsiness. During the period of treatment should refrain from driving vehicles and occupation of other potentially hazardous activities that require high concentration and psychomotor speed reactions.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not higher than 25 C in a dry place, protected from light.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Inside. Children older than 15 years and adults – 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The maximum daily dose – 4 tablets. The course of treatment no more than 5 days.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Rinzai |










There are no reviews yet.