- No products in the cart.
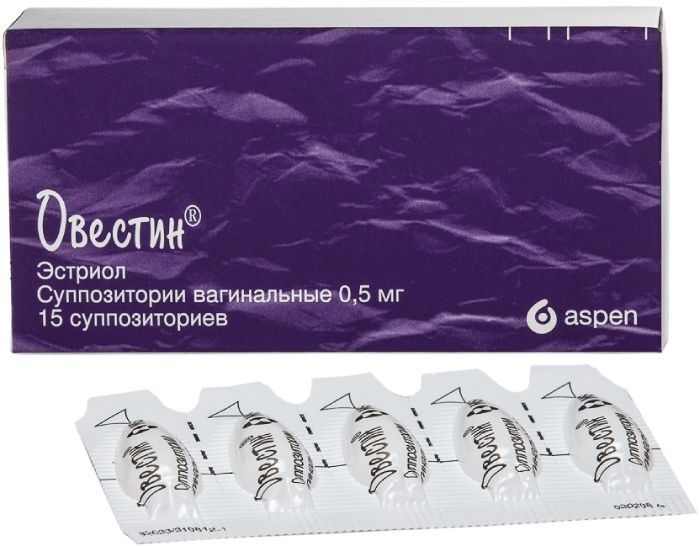
Ovestin suppositories vaginas. 0.5mg 15 pc
$26.67
Ovestin suppositories vaginas. 0.5mg 15 pc
Description
Composition
Active substance:
1 suppository contains: 0.5 mg of estriol.
Excipients:
Witepsol S58 2,4995 g
Description:
Suppositories are torpedo-shaped, white to cream-colored. The surface and uniform longitudinal section.
Product form:
Vaginal suppositories 0.5 mg. 5 suppositories in a bilateral contour blister PVC / PE. 3 outline package together with instructions for use placed in a cardboard box.
Contraindications
• Mounted with a history of or suspected breast cancer. • Diagnosed estrogen-dependent tumor or suspicion on them (eg, endometrial cancer). • Vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology. • Untreated endometrial hyperplasia. • The presence of venous thrombosis in the present and in history (deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism). • Confirmed thrombophilia (e.g., protein C deficiency, protein S or antithrombin (see. The section “Special instructions”)). • thrombosis (venous and arterial) and thromboembolism currently or history (including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke..), Cerebrovascular disorders; state prior thrombosis (in t. h., transient ischemic attack, angina) currently or history. • Liver disease in the acute stage of the disease or a history of liver, after which liver function tests have not returned to normal. • installed sensitivity to the active agent or any of the excipients of the drug. • Porphyria.
Carefully
With caution (under careful medical supervision) Ovestin® drug should be used if there are any of the following diseases or conditions, or these diseases or conditions noted above and / or deteriorated during the preceding pregnancy or prior hormonal treatment conducted (as they may recur or worsen during treatment with Ovestin®):
Leiomyomas (uterine fibroids), or endometriosis.
Risk factors for thromboembolism (see. “Special Instructions” section).
Risk factors for estrogen-tumor, e.g., the first degree of heredity for breast cancer.
Arterial hypertension.
Benign tumors of the liver (e.g., hepatic adenoma).
Diabetes with diabetic angiopathy or without it.
Cholelithiasis.
Jaundice (including history during previous pregnancy).
Liver failure.
Migraine or (severe) headache.
Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Endometrial hyperplasia in history (see. “Special Instructions” section).
Epilepsy.
Bronchial asthma.
Otosclerosis.
Family hyperlipoproteinemia.
Pancreatitis.
Dosage
0.5 mg
Indications
• Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for the treatment of mucosal atrophy of the lower genital tract related to estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women. • Pre- and post-operative therapy in postmenopausal women shown in surgical interventions during vaginal access. • As an auxiliary diagnostic tool in the preparation of atrophic cervical smear pattern.
Interaction with other drugs
In clinical practice were observed interaction between the drug and Ovestin® other drugs. Estrogen metabolism may be enhanced when used in combination with compounds that induce the enzymes involved in the metabolism of drugs, in particular, cytochrome P450 enzymes, e.g., such as anticonvulsants (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine) and antimicrobial agents (e.g. rifampicin, rifabutin, nevirapine, efavirenz). Ritonavir and nelfinavir exhibit inducing properties when used in combination with steroid hormones. Herbal preparations containing St. John’s wort (Hypericum Perforatum), may induce estrogen metabolism. Increased estrogen metabolism may lead to a decrease in their clinical effect. Estriol enhances the effect of lipid-lowering drugs; It weakens the effects of male sex hormones, anticoagulants, antidepressants, diuretics, antihypertensive, hypoglycemic drugs. Medicines for general anesthesia, narcotic analgesics, anxiolytics, some antihypertensive drugs, ethanol reduces the effectiveness of the drug. Folic acid and thyroid medications increase the effect of estriol.
Overdose
Acute toxicity of estriol in animals is very low. Overdosing Ovestin® preparation for vaginal administration is unlikely. However, in case of contact with large quantities of the gastro-intestinal tract may develop nausea, vomiting, and cessation of bleeding in women. Specific antidote is not known. If necessary, symptomatic treatment.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Estrogen.
Pharmacodynamics:
The drug Ovestin® contains estriol – an analog of the natural female hormone. He makes up for deficiency of estrogen in postmenopausal women and reduces the symptoms of menopause. Estriol is most effective in the treatment of genitourinary disorders. In the case of mucosal atrophy lower parts of the urogenital tract estriol helps normalize epithelial urinary tract and promotes the restoration of the normal microflora and the physiological pH of the vagina. As a result, it improves resistance to urinary tract epithelial cells to infection and inflammation, reducing such complaints as pain during intercourse, dryness, itching of the vagina, it decreases the likelihood of vaginal infections, urinary tract infections, contributes to the normalization of urination and prevents urinary incontinence. In contrast to other estrogens estriol has a short duration of action, as in the nuclei of endometrial cells it is held for a short time. It is assumed that a single dose daily dose does not cause endometrial proliferation. Therefore, no cyclic administration of progestogen and no cancellation occurs bleeding. In addition, it is shown that estriol does not increase mammographic density.
Pharmacokinetics:
Intravaginal administration of estriol ensures optimal bioavailability at the site of action. Estriol is also absorbed and enters the bloodstream, which is manifested a rapid increase in the concentration of unbound estriol in plasma. The maximum plasma concentration observed after 1-2 hours after administration. In plasma, almost all (90%) estriol is bound to albumin and, unlike other estrogen hardly associated with binding globulin sex hormone. Metabolism estriol is mainly in the transition in the conjugated and unconjugated state when enteric-hepatic circulation. Estriol, being the end product of metabolism is mainly excreted in urine in the bound form. Only a small fraction (about 2%) is excreted in feces mainly as unbound estriol. The half-life is approximately 6-9 hours. After vaginal administration of 0.5 mg estriol maximum concentration Cmax was approximately 100 pg / ml, a minimum concentration Cmin – about 25 pg / ml and the average concentration SSR – about 70 pg / ml. After 3 weeks of daily administration of 0.5 mg vaginal estriol Csr value decreased to 40 pg / ml.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ovestin® drug is contraindicated during pregnancy. In case of pregnancy during therapy with Ovestin® treatment should be lifted immediately. The results of most epidemiological studies conducted to date in relation to unintended effects of estrogen on the fetus showed no teratogenic or foetotoxic effects. The drug Ovestin® not recommended during breastfeeding. Estriol is excreted in breast milk and may reduce the formation of milk.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Without recipe.
side effects
As in the case of any other drug that is applied to mucosal surfaces, suppositories Ovestin® can sometimes cause local irritation or itching. Sometimes there may be a sensitivity, tension, pain, enlargement of the mammary glands. These undesirable reactions are usually short-lived and passing, but at the same time may indicate the use of too high a dose. Also found: acyclic spotting, bleeding “breakthrough”, metrorrhagia. It reported other adverse reactions that have arisen on Estrogen or combined therapy of estrogen and progestogen.
Violations of the liver and biliary tract: – Gallstone disease.
Benign, malignant neoplasms and unspecified (including cysts and polyps): – estrogen-dependent benign or malignant neoplasia, including endometrial cancer (for more information, see. in the “Contraindications” and “Special instructions”).
Mental disorders – Dementia in the beginning of HRT continuously after 65 years (. See “Special Instructions”).
Violations by the genitals and breast: – Increased libido. Violations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: – chloasma, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, hemorrhagic purpura.
There are data on the risk of developing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, the risk of venous thromboembolism, the risk of coronary heart disease, the risk of ischemic stroke (details are provided in the “Special Instructions”).
special instructions
• For the treatment of menopausal symptoms HRT should be started only on the symptoms that adversely affect quality of life. In all cases, at least once a year to carry out a thorough risk assessment and the use of hormone replacement therapy and the treatment should be continued only for such time as the benefit outweighs the risk. • There is limited evidence of the risk of HRT in the treatment of premature menopause. Due to the low absolute risk in younger women, the risk benefit ratio have more favorable than in older.
Medical examination / observation • Before starting or resuming HRT need to collect detailed personal and family history. Guided by the received history, contraindication and warnings of use, it is necessary to carry out a clinical examination (including pelvic examination and mammary glands). During treatment, it is recommended to carry out periodic medical examinations, the frequency and nature of which are unique. Women should be informed of the need to doctor message on changes in the mammary glands (see. Below “Breast cancer”). Studies, including appropriate imaging techniques, such as mammography, be carried out in accordance with accepted standards currently examination and depending on each case.
Reasons for immediate discontinuation
Therapy should stop in case of contraindications and under the following conditions: • Jaundice or deterioration of liver functions. • Significant increase in blood pressure. • The emergence of migraine headache type. • Pregnancy.
Endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma • To prevent endometrial stimulation daily dose should not exceed 1 suppository (0.5 mg estriol). Do not use the maximum dosage for more than 4 weeks. Furthermore, in one epidemiological study it found that long reception estriol in low doses, administered orally, intravaginally but may increase the risk of endometrial cancer. The risk increases with duration of treatment and returned to baseline values one year after drug withdrawal. In general, the risk of minimally invasive and highly differentiated tumors. Vaginal bleeding in all cases require a survey. The patient should be informed about the need to contact your doctor in case of vaginal bleeding.
Breast cancer • Hormone replacement therapy may increase mammographic density. This may complicate the radiological detection of breast cancer. Clinical studies have shown that the probability of an increase in mammographic density is lower in women treated with estriol than in women treated with other estrogens. • Pooled evidence suggests an increased risk of breast cancer in women receiving combination therapy of estrogen and progestogen and possibly estrogen monotherapy. • For women receiving combination therapy of estrogen and progestogen over 5 years, an increase in breast cancer risk by 2 times. • Monotherapy with an increased risk of estrogen is significantly lower than when combined with progestogen. • The level of risk depends on the duration of HRT. • It is not known whether the drug is Ovestin® the same risk. In a recently conducted by population-based case-control study involving 3345 women with breast cancer and 3454 women invasive cancer in the control group showed that the use of estriol, unlike other estrogen was not associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer. Therefore, it is important that the risk of developing breast cancer was discussed with the patient and is correlated with the known use of HRT.
Ovarian cancer • Ovarian cancer develops much rarer than breast cancer. Prolonged estrogen monotherapy (at least 5-10 years) was associated with a small increased risk of ovarian cancer. Some studies suggest that combination HRT may increase the risk of ovarian cancer in a similar way, or only slightly. It is not known whether the risk differs with the chronic administration of low level of estrogen (such as Ovestin®) from that of other estrogen monotherapy.
Venous thromboembolism • HRT is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), ie deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism is 1.3 – 3 times. The probability of VTE is higher in the first year of HRT use than at a later date. It is not known whether the drug Ovestin® the same risk is. • Patients with confirmed thrombophilia risk of VTE is highest, as HRT may further increase it. In this regard, hormone replacement therapy is contraindicated such women (see. The section “Contra ‘). • Generally recognized risk factors for VTE is estrogen, older age, extensive surgery, prolonged immobilisation, obesity (BMI> 30 kg / m2), pregnancy / postpartum period, systemic lupus erythematosus, and cancer. There is no consensus about the possible role of varicose veins in VTE development. After any surgery, it is necessary to carry out prevention of VTE. If prolonged immobilization associated with elective surgery, it is necessary to temporarily cancel HRT for 4-6 weeks prior to surgery. Treatment should be resumed after the woman begins to walk. • For women who are already receiving anticoagulant treatment require careful consideration of the benefit-risk of HRT. • If Ovestin® designated as “pre- and post-operative treatment …”, should consider prevention of thrombosis. • In the absence of VTE in history, but in the presence of thrombosis at a young age, the next of kin of the patient it is possible to propose a screening examination, after discussing all its limitations (screening reveals only a series of thrombophilic disorders). In identifying thrombophilic defect is not relevant disease relatives or detection “heavy” defect (e.g., Antithrombin deficiency, Protein S or Protein C, or a combination of these defects) HRT is contraindicated. • If, after the start of treatment Ovestin® developing VTE, the treatment with the drug should be discontinued. Patients should be informed about the need for immediate treatment to the doctor, if they feel the possible symptoms of thromboembolism (eg, painful swelling of the legs, sudden chest pain, shortness of breath).
Coronary heart disease (CHD) • In a randomized, controlled trials have not produced the results that would indicate that a combination therapy of estrogen and progestogen and estrogen monotherapy may prevent the development of myocardial infarction in women with CHD and without it. Estrogen: – According to the data from randomized controlled trials in women with hysterectomy risk of coronary heart disease when estrogen alone does not increase. • The risk of coronary heart disease increases slightly with the combined estrogen and progestogen hormone replacement therapy in patients older than 60 years.
Ischemic stroke • Combined estrogen and progestogen therapy and monotherapy with estrogens are associated with increased risk of ischemic stroke by 1.5 times. Relative risk with age and with time after menopause does not change. However, the baseline risk of stroke is largely dependent on the age, and the overall risk of stroke with HRT increases with age. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke in HRT does not increase.
Other conditions • Estrogens may cause fluid retention, and therefore patients with impaired renal function and cardiovascular insufficiency should be carefully monitored. • Estriol is a weak antagonist of gonadotropin and has no other significant effects on the endocrine system. • Cognitive function on HRT does not improve. The certificate of an increased risk of dementia in women who began to use combination therapy or monotherapy in continuous operation after 65 years.
Effects on ability to drive and use other mechanisms
Ovestin® effect of the drug on the concentration and attention were observed.
Storage conditions
At a temperature of 2-25 C in a dry place, protected from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Ovestin® suppositories should be inserted into the vagina at night before bed. • In the treatment of atrophy of the mucosa of the lower genital tract: one suppository daily for the first week, followed by a gradual reduction of the dose based on relieving the symptoms, to achieve the maintenance dose (i.e., 1 suppository twice a week). • Pre- and postoperative therapy in women with postmenopausal vaginal access surgery: 1 suppository daily for 2 weeks prior to surgery; 1 суппозиторий дважды в неделю в течение 2 недель после операции. • С диагностической целью при неясных результатах цитологического исследования с шейки матки: 1 суппозиторий через день в течение недели перед взятием следующего мазка. Пропущенную дозу необходимо ввести в этот же день, как только больная вспомнит об этом (доза не должна вводиться дважды в день). В дальнейшем аппликации проводят в соответствии с обычной схемой дозирования. При начале или при продолжении лечения постменопаузальных симптомов необходимо применять наименьшую эффективную дозу в течение наиболее короткого промежутка времени. У женщин, не получающих ЗГТ, или женщин, которые переводятся с непрерывного перорального приёма комбинированного препарата для ЗГТ, лечение препаратом Овестин® можно начинать в любой день. Женщины, которые переходят с циклического режима приёма препаратов для ЗГТ, должны начинать лечение препаратом Овестин® через одну неделю после отмены препаратов ЗГТ.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Ovestin |









There are no reviews yet.