- No products in the cart.
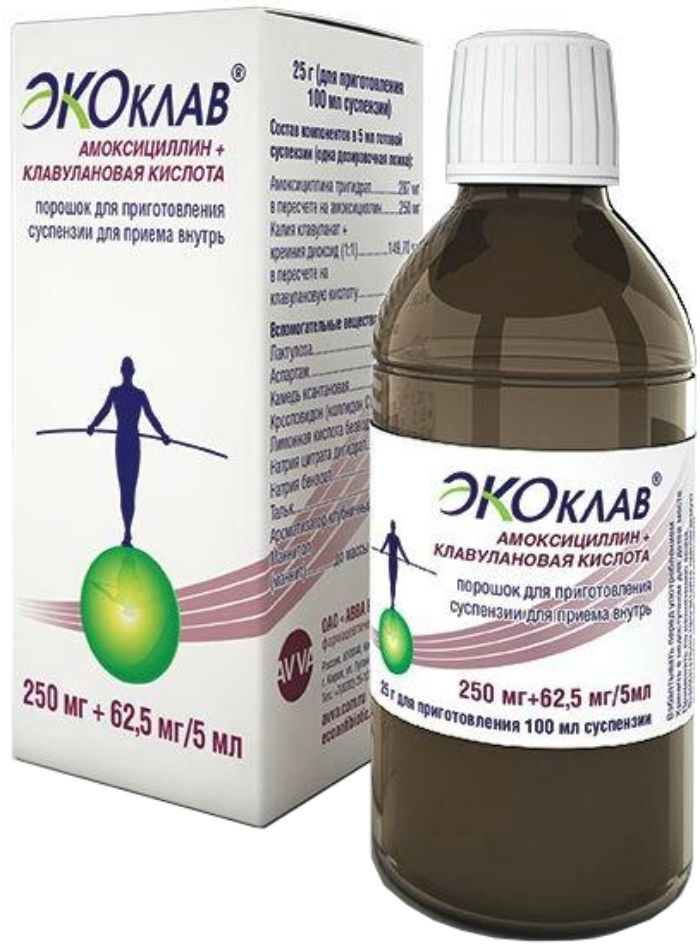
Ekoklav prig.susp.dlya powder for oral 62,5mg + 250mg / 5ml vial 1 piece 25d with measuring spoon 2-sided
Ceftazidime powder for solution for injection vial 1 piece 1d Rafarma
$2.07

Complex extracts tansy and walnut leaves caps 40 pcs WTF
$5.62
$5.57
Ekoklav prig.susp.dlya powder for oral 62,5mg + 250mg / 5ml vial 1 piece 25d with measuring spoon 2-sided
SKU: 1121396269 Categories: Antibiotics, Antibiotics, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, Medicaments Tags: ABBA RUS, Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid
Description
Composition
Active substance:
Each 5 ml of the finished suspensions (one dosing spoon) contain:
Amoxycillin trihydrate, (calculated as amoxicillin) 250 mg
potassium clavulanate (in terms of clavulanic acid) 62.5 mg
Excipients:
Lactulose 400 mg
5.5 mg of aspartame
Colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil) 16.885 mg
Xanthan gum 10.0 mg
Crospovidone (Kollidon CL-M) 28,1 mg
Citric acid anhydrous 2.165 mg
Sodium citrate dihydrate 8.335 mg
2,085 mg Sodium benzoate
Talc 25.0 mg
Orange flavor 4.0 mg
Mannitol (mannitol) Prior to powder mass 1.25 g
Description:
The powder is white to off-white with a faint fruity odor. After dissolution in water slurry is formed from nearly white to light yellow color with a fruity odor.
Product form:
powder for suspension for oral administration 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 ml.
25 g of brown glass bottles of 125 ml and labeled with a screwed plastic cap.
Each vial together with two-way dispensing spoon (small capacity of 2.5 ml, large – 5 ml) and instructions for use placed in a pile of cardboard.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics), infectious mononucleosis, jaundice episodes or abnormal liver function as a result of amoxycillin / clavulanic acid history, phenylketonuria (containing aspartame).
Carefully.
Severe hepatic insufficiency, gastrointestinal tract (including a history of colitis associated with the use of penicillins), chronic renal insufficiency.
Dosage
250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 ml
Indications
Infectious-inflammatory diseases caused by pathogens susceptible to the drug:
• Lower respiratory tract infections (bronchitis, pneumonia);
• infection of upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media);
• infections of the genitourinary system and the pelvic organs (pyelonephritis, pyelitis, cystitis, urethritis, bacterial prostatitis, cervicitis, salpingitis, oophoritis, endometritis, bacterial vaginitis, septic abortion, chancroid, gonorrhea);
• Skin and soft tissue infections (erysipelas, impetigo, secondarily infected dermatitis, abscesses, cellulitis, wound infection);
• bone and joint infections (osteomyelitis).
Interaction with other drugs
It is not recommended to apply a combined formulation of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid concurrently with probenecid. Probenecid reduces the tubular secretion of amoxicillin, therefore co-administration may lead to an increase and persistence in the serum concentration of amoxicillin, the serum concentration of clavulanic acid is not changed.
Diuretics, allopurinol, phenylbutazone, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs that block tubular secretion, increase the concentration of amoxicillin (Clavulanic acid is derived largely by glomerular filtration).
Antacids, glucosamine, laxatives slow down and reduce the absorption of amoxicillin; ascorbic acid – increases.
Allopurinol increases the risk of skin rash.
As with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, the combined formulation of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid may reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, and patients need to be informed about this.
The literature describes the rare cases of increased international normalized ratio (INR) in patients with concomitant use of warfarin and acenocoumarol or amoxicillin. If necessary, co-administration of the combination preparation of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid with indirect anticoagulants prothrombin time and INR should be monitored closely in the appointment or revocation of the drug.
Overdose
Symptoms: violation of the functions of the gastrointestinal tract and water-electrolyte balance.
Treatment: symptomatic. Hemodialysis is effective.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
Antibiotic – penicillin semisynthetic + beta-lactamase inhibitor.
Pharmacological properties:
Combined preparation of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, – beta-lactamase inhibitor. Amoxicillin – a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic; bactericidal effect by inhibiting bacterial cell wall susceptible to the growth stage of protein synthesis. Clavulanic kiclota has high affinity for bacterial beta-lactamases, and forms a stable complex with them. Thus, biodegradation amoxicillin beta-lactamases is prevented, and the bactericidal activity of the antibiotic is maintained. Clavulanic kiclota inhibits beta-lactamase II-V type classification Richmond-Sykes and not active against beta-lactamase I type produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia spp., Acinetobacter spp.
Combined preparation of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid according to the results of tests in vitro and clinical research is active against the following microorganisms:
Gram positive aerobic bacteria:
• Staphylococcus aureus (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
Gram-negative aerobic bacteria:
• Enterobacter spp. (Despite the fact that most of the resistant strains of Enterobacter in vitro, the effectiveness of the drug is clinically proved in the treatment of this agent caused by infectious diseases of the urinary system);
• Escherichia coli (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Haemophilus influenzae (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Klebsiella spp. (All known strains produce beta-lactamase);
• Moraxella catarrhalis (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase).
According to the results of in vitro studies have demonstrated sensitivity to the combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid following microorganisms:
Gram positive aerobic bacteria:
• Enterococcus faecalis **;
• Staphylococcus epidermidis (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Staphylococcus saprophyticus (strains producing and not producing betalactamase);
• Streptococcus pneumoniae ** (beta-lactamase does not produce);
• Streptococcus pyogenes ** (beta-lactamase does not produce);
• Streptococcus spp. group viridans ** (beta-lactamase does not produce).
Gram-negative aerobic bacteria:
• Eikenella corrodens (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae ** (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Proteus mirabilis ** (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase).
Anaerobic microorganisms:
• Bacteroides spp, including Bacteroides fragilis (strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase).;
• Fusobacterium spp. (Strains producing and not producing beta-lactamase);
• Peptostreptococcus spp. (Beta-lactamase does not produce).
NOTE: ** – (clinically proven efficacy of amoxicillin in the treatment of a number of infections caused by these pathogens).
Pharmacokinetics:
Suction. After oral administration, the two components of the drug is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absorption of the active ingredients of the drug is optimum when its reception at the beginning of the meal.
After oral administration at a dose of 125 mg + 31.25 mg:
• Cmax amoxicillin – 1.96 ug / ml of clavulanic acid – 0.77 g / ml;
• Tmax amoxicillin – 1.5 hours, clavulanic acid – 1.0 hours;
• AUC amoxicillin – 9.19 mg • h / L clavulanic acid – 2.69 mg • h / L.
In applying the drug serum concentration of amoxycillin are similar to those after oral administration of equivalent doses of amoxicillin.
Distribution. Both components are characterized by good drug distribution volume – therapeutic concentrations of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are in different organs and tissues, interstitial fluid: lung, middle ear, abdominal, pelvic organs (prostate, uterus, ovary), skin; fat, bone and muscle tissues; pleural, synovial and peritoneal fluids; plasma, bile, purulent discharge, sputum, bronchial secretions.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid have a moderate degree of binding to plasma proteins, respectively, 18% and 25%.
Both components of the drug to penetrate through the placental barrier, but data about the negative effects on the fetus has not been published.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid in low concentrations found in breast milk.
Metabolism, excretion. Approximately 60-70% of amoxycillin kidneys displayed: by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration rate unchanged, about 10-25% in the form of inactive penitsilloevoy acid. Clavulanic acid is extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted by glomerular filtration (40-65%), partially in the form of metabolites.
A smaller part of the intestine is displayed.
In renal insufficiency, the clearance of amoxicillin with clavulanic acid is reduced, however the dose required correction.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Combination drug of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid during pregnancy is recommended to be prescribed only in cases where the expected benefit from taking it to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
The drug can be used during breastfeeding. With the exception of the risk of sensitization, associated with the penetration in the breast milk of trace amounts of the active ingredients of this preparation, no other adverse effects in infants who are breastfed, found there was no
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
Prescription.
side effects
The drug was well tolerated. Side effects are rare, are mostly mild and transient in nature.
• From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastritis, stomatitis, glossitis, cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, liver failure (more common in the elderly, women, long-term therapy), colitis (including pseudomembranous), black “hairy” tongue, dark tooth enamel, the increase in “liver” transaminases, bilirubin and increased content of alkaline phosphatase activity.
• From the side of hematopoiesis: reversible increase of prothrombin time and bleeding time, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia.
• Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, hyperactivity, anxiety, changes in behavior, convulsions.
• Allergic reactions: urticaria, erythematous rash, erythema multiforme, anaphylaxis, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), allergic vasculitis syndrome similar to serum sickness, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
• On the part of the kidney and urinary tract: interstitial nephritis, crystalluria, haematuria.
Other: candidiasis, superinfection development.
special instructions
The severity of gastrointestinal symptoms decreased while taking the drug at the beginning of the meal.
In exchange treatment is necessary to control the state functions of blood, liver and kidneys.
Perhaps the development of superinfection due to the selection of resistant forms of the pathogen.
It may be identified false positive results in the determination of glucose in urine.
In this case it is recommended to apply glyukozoksidantny method of determining the concentration of glucose in the urine.
In patients with increased sensitivity to penicillins, possible allergic cross-reaction with cephalosporin antibiotics.
In the case of suspected infectious mononucleosis drug should not be used as in patients with the disease Amoxicillin can cause morbilliform rash, making it difficult to diagnose the disease.
Given the likelihood of adverse effects on the central nervous system, caution should be exercised when driving and operating machinery.
Storage conditions
In a dry, dark place at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C.
The finished suspension was stored at 2 ° C to 8 ° C in a tightly closed flask for 7 days.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Inside. The mode set individually depending on the patient’s weight, the severity and localization of infection and susceptibility.
Minimum course of antibacterial therapy – 5 days. Treatment should not be continued longer than 14 days without a review of the clinical situation. Duration of treatment of uncomplicated acute otitis media is 5-7 days in children up to 2 years – 7-10 days.
A single dose is determined depending on the age and body weight (calculated on amoxicillin):
• children up to 3 months – 30 mg / kg / day in 2 divided doses;
• Children from 3 months of age and older:
– low-dose (for treatment of skin and soft tissue infections and chronic tonsillitis) –
20 mg / kg / day in 3 divided doses;
– high-dose (for the treatment of otitis media, sinusitis, lower respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections) – 40 mg / kg / day in 3 divided doses.
Children weight 40 kg or more should be administered a dose as adults.
The suspension can be used in adults with difficulty swallowing.
The recommended dosing regimen for adults: 20 ml of the suspension at a dosage of
125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of the suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 ml 2-3 times a day.
The maximum daily dose of amoxicillin for adults and children over 12 years – 6 g,
for children up to 12 years – 45 mg / kg body weight.
The maximum daily dose of clavulanic acid for adults and children over 12 years – 600 mg,
for children up to 12 years – 10 mg / kg body weight.
Patients with impaired renal function:
Correction doses based on the maximum recommended dose of amoxycillin and creatinine clearance value.
• Children
Creatinine clearance was 30 ml / min the dose correction is not required;
Creatinine clearance of 10-30 ml / min – 15 mg / 3.75 mg / kg, 2 times a day with a maximum dose
500 mg + 125 mg (20 ml of a suspension at a dose of 125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of the suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 mL), 2 times a day;
Creatinine clearance less than 10 mL / min – 15 mg / 3.75 mg / kg 1 time a day, the maximum daily dose of 500 mg + 125 mg (20 ml of a suspension at a dose of 125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 ml);
• Adults
Creatinine clearance was 30 ml / min the dose correction is not required;
Creatinine clearance of 10-30 ml / min – 500 mg + 125 mg (20 ml of a suspension at a dose
125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of the suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 mL), 2 times a day;
creatinine clearance less than 10 mL / min – 500 mg + 125 mg (20 ml of a suspension at a dose
125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of the suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 mL) 1 time a day;
Patients on hemodialysis:
Correction doses based on the maximum recommended dose of amoxicillin • Children – 15 mg / 3.75 mg / kg 1 time a day.
Before hemodialysis should take one additional dose of 15 mg / 3.75 mg / kg.
To restore the concentrations of active ingredients of the drug in the blood of a second additional dose of 15 mg / 3.75 mg / kg should be taken after the dialysis session.
• Adults – 500 mg + 125 mg (20 ml of a suspension at a dose of 125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml or 10 ml of the suspension at a dosage of 250 mg + 62.5 mg / 5 ml) once every 24 hours.
Additional 1 dose during the dialysis session and one dose at the end of the dialysis session (to compensate for the reduction in serum concentrations of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid)
A method for preparing the suspension:
The suspension is prepared immediately prior to use.
Powder in vial pre-shaken, then adding a small amount of boiled and cooled to room temperature, water was stirred to give a uniform suspension, and then water was added to the mark on the vial. For accurate dosing suspension dosage should use two way spoon which need to rinse well with water after each application. After dilution of the slurry should be stored no longer than 7 days in the refrigerator but do not freeze.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | ABBA RUS |








There are no reviews yet.