- No products in the cart.
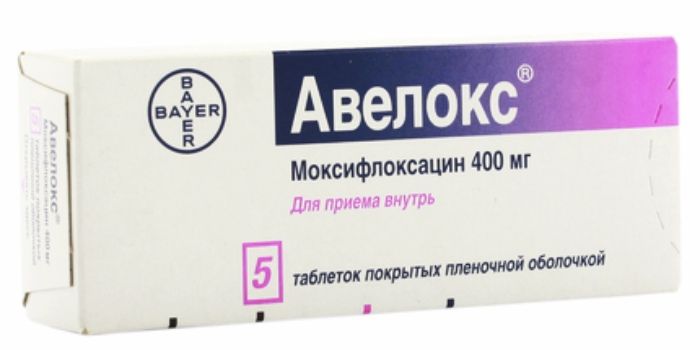
Avelox tab n / 400mg film about 5 pc
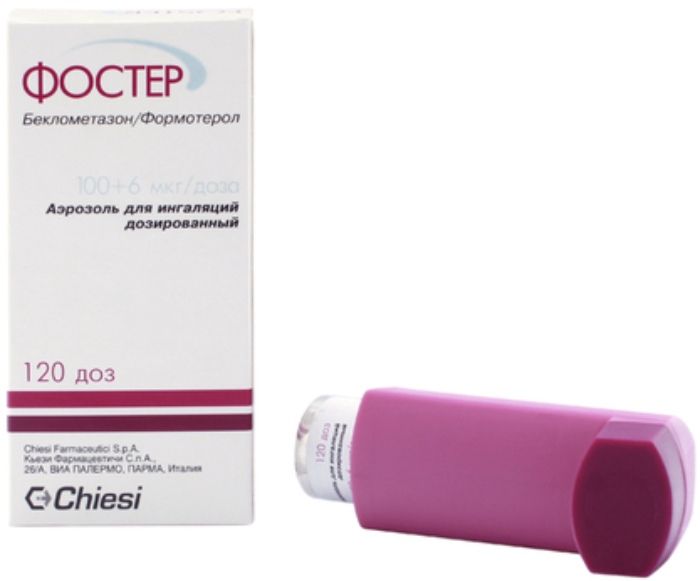
Foster spray ing. scrapper. 6mkg + 0.1mg / dose 120doz
$50.90
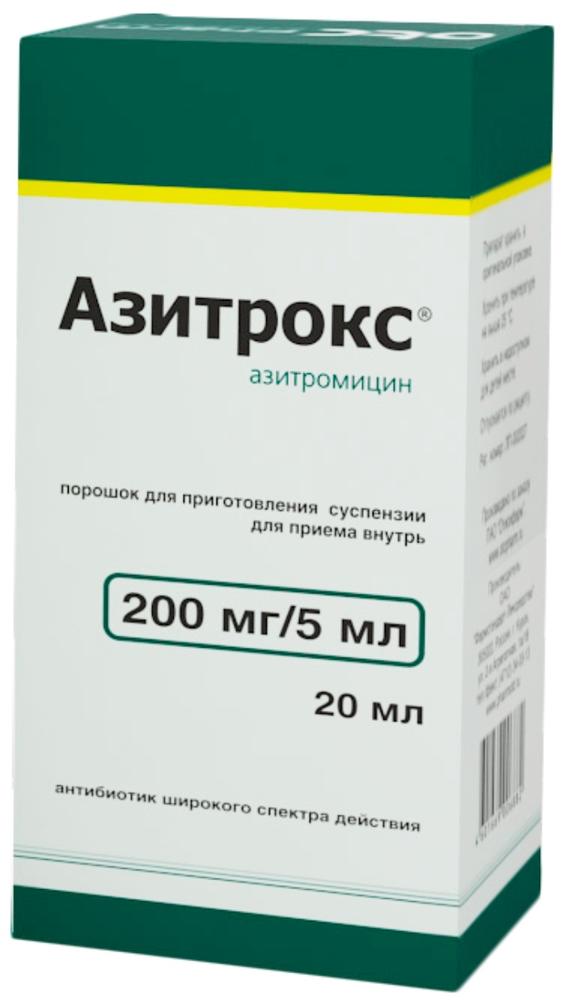
Azitroks prig.susp.dlya powder for oral 200mg / 5ml vial 15.9g one piece with the measuring spoon and a pipette
$7.09
$17.38
Avelox tab n / 400mg film about 5 pc
SKU: 1993714250 Categories: Antibacterial, Antibiotics, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, Medicaments Tags: Bayer Pharmaceuticals, moxifloxacin
Description
Composition
Active substance:
1 tablet contains – moxifloxacin hydrochloride is 436.8 mg, equivalent to 400.0 mg of moxifloxacin.
Excipients:
Microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stea- rat, film coating – hypromellose, iron oxide red dye, macrogol 4000, titanium dioxide.
Description:
Pink matte oblong bevelled biconvex tablets coated with a film cover Tide, with an engraving «BAYER» on one side and «M400» again in another party.
Product form:
Tablets, film-coated, 400 mg.
5 tablets per blister with aluminum foil and PA / Al / PVC foil or aluminum and PP.
1 or 2 blisters together with instructions for use in a cardboard package, or 7 tablets in blister with aluminum foil and PA / Al / PVC or PP and aluminum foil.
1 blister together with instructions for use in a cardboard package.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin, other quinolones or to any other component of the drug, the age of 18, pregnant and breastfeeding, history of tendon pathology, which developed as a result of treatment with antibiotics of the quinolone series. In preclinical and clinical studies were observed after administration of moxifloxacin change of electrophysiological parameters of the heart, expressed in a lengthening of the QT interval. In this regard, moxifloxacin is contraindicated in patients following categories: acquired or congenital documented elongation interval QT, electrolyte abnormalities, particularly hypokalemia uncorrected; clinically significant bradycardia; clinically significant heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction; a history of arrhythmias, accompanied by clinical symptoms. Moxifloxacin should not be used with other drugs that prolong the QT interval. Due to the presence of lactose drug, its reception is contraindicated in congenital lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption. Due to the limited amount of clinical data moxifloxacin use is contraindicated in patients with impaired liver function (class C Child-Pugh classification) and patients with elevated transaminase more than five times the upper limit of normal.
C. CARE – diseases of the central nervous system (including suspicious regarding CNS involvement..) Predisposing to seizures, and reducing the threshold for seizure activity; – in patients with psychosis and / or mental health history; – in patients with potentially proarrhythmic conditions (especially women and elderly patients) such as acute myocardial ischemia and heart failure; – myasthenia gravis; – in patients with cirrhosis of the liver; – while receiving with drugs to lower the potassium content. – in patients with a genetic predisposition, or actual presence of deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Dosage
400 mg
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by susceptible to moxifloxacin microorganisms: Acute sinusitis, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, uncomplicated skin infections and subcutaneous structures, community-acquired pneumonia, including CAP which pathogens are microbial strains with multiple resistance to antibiotics *, complications of infections of skin and subcutaneous structures (including infected diabetic foot) complicated intraabdominal infections, including polymicrobial infection, t m including intra-abdominal abscesses, Uncomplicated inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (including salpingitis and endometritis).
* Streptococcus pneumoniae with multiple resistance to antibiotics include strains that are resistant to penicillin, and strains resistant to two or more antibiotics from the groups such as the penicillins (with MIC> 2, ug / ml), cephalosporins II generation (cefuroxime), macrolides, tetracyclines and trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole. It is necessary to take into consideration existing official guidance on the rules of use of antibacterial agents.
Interaction with other drugs
When combined with atenolol, ranitidine, calcium-containing additives, theophylline, cyclosporin, oral contraceptives, glibenclamide, itraconazole, digoxin, morphine, probenecid (Confirmed the absence of clinically significant interactions with moxifloxacin) correction dose is not required.
Drugs prolonging the QT interval.
It will be appreciated the possible additive effect of QT interval elongation of moxifloxacin and other preparations, which influence the lengthening of the interval QT. Due to the joint application of moxifloxacin and drugs affecting the lengthening of the interval QT, it increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias, including polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (torsade de pointes). Contraindicated for concomitant use of moxifloxacin with the following drugs affecting lengthening the interval QT: antiarrhythmic drugs of class IA (quinidine, gidrohinidin, disopyramide, etc.); antiarrhythmic drugs of class III (amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide et al.); antipsychotics (phenothiazine, pimozide, sertindole, haloperidol, sultopride et al.); tricyclic antidepressants; antimicrobials (sparfloxacin, erythromycin (i.v.), pentamidine, antimalarials particularly halofantrine); antihistamines (terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine); others (cisapride, vincamine (intravenously), bepridil, difemanil). Antacids, multivitamins and minerals.
Receiving moxifloxacin simultaneously with antacids, multivitamins and minerals can lead to malabsorption moxifloxacin, due to formation of chelate complexes with multivalent cations contained in these preparations. As a result, the concentration of moxifloxacin in plasma may be significantly lower than desired. In this regard, antacids, anti-retroviral agents (e.g., ddI) and other preparations containing magnesium or aluminum, sucralfate and other drugs containing iron or zinc, to be applied at least 4 hours before or 4 hours after ingestion moxifloxacin.
Warfarin.
If concomitant use of warfarin and prothrombin time, other blood coagulation parameters are not changed.
Changing the value of the INR.
Patients treated with anticoagulants in combination with antibiotics, including moxifloxacin, there are cases increase anticoagulant activity of anticoagulant drugs. The risk factors are the presence of an infectious disease (and the accompanying inflammatory process), age and general condition of the patient. Despite the fact that the interaction between moxifloxacin and warfarin was not found in patients receiving combined treatment with these drugs, it is necessary to carry out monitoring of INR and adjust the dose of anticoagulants if necessary.
Digoxin.
Moxifloxacin and digoxin did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetic parameters of each other. In the application of repeated doses of moxifloxacin maximum concentration of digoxin was increased by approximately 30%, while the value of the area under the curve “concentration-time» (AUC) and the minimum concentration of digoxin did not change. Activated carbon.
With simultaneous application of activated carbon and moxifloxacin oral dose of 400 mg systemic bioavailability is reduced by more than 80% as a result of inhibition of absorption. In the case of an overdose of activated carbon at an early stage suction prevents further increase the systemic exposure.
Overdose
There are limited data on overdose of moxifloxacin. Not observed any side effects when used at a dose of moxifloxacin to 1200 mg once daily and 600 mg for 10 days or more. In case of overdose should be guided by the clinical picture and symptomatic supportive therapy with ECG monitoring. The use of activated charcoal immediately after oral administration of the drug can help prevent excessive systemic exposure of moxifloxacin in cases of overdose.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological group:
The antimicrobial agent – fluoroquinolone.
Pharmacological properties:
Antimicrobial broad-spectrum antibacterial action.
Pharmacodynamics:
Mechanism of action
Moxifloxacin – bactericidal antimicrobial broad-spectrum 8-metoksiftorhinolon.
The bactericidal action of moxifloxacin due to inhibition of bacterial topoisomerase II and IV, which disrupts the replication process of DNA biosynthesis and repair transcription microbial cells and, consequently, to the death of the microbial cells.
The minimum bactericidal concentration of moxifloxacin generally comparable to its minimum inhibitory concentration.
mechanisms of resistance
The mechanisms leading to the development of resistance to penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, macrolides and tetracyclines do not affect the antibacterial activity of moxifloxacin. Cross resistance between these groups antimicrobials and moxifloxacin not marked. Until now, as no cases of plasmid stability. The overall incidence of resistance is very low. Resistance to moxifloxacin develops slowly by multiple mutations. Repeated exposure of moxifloxacin on microorganisms at concentrations less than the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) accompanied by a slight increase in the MIC. There are cases of cross-resistance to quinolones. Nevertheless, some resistant to other quinolones and gram-positive anaerobic bacteria remain sensitive to moxifloxacin.
The addition to the structure of the molecule the moxifloxacin methoxy group at position C8 moxifloxacin increases the activity and decreases the formation of resistant mutant strains of Gram-positive bacteria. Joining bitsikloaminovoy group at C7 prevents the development of active efflux mechanism of resistance to fluoroquinolones. Moxifloxacin is active in vitro against a broad spectrum of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, anaerobes, atypical acid-fast bacteria and bacteria such as Mycoplasma spp., Chlamydia spp., Legionella spp., And bacteria resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics and macrolide.
Impact on the human intestinal microflora
In two trials conducted on volunteers, the following changes were noted intestinal microflora after oral administration of moxifloxacin. Escherichia coli, a decrease concentrations
Bacillus spp., Bacteroides vulgatus, Enterococcus spp., Klebsiella spp., And anaerobic bacteria Bifidobacterium spp., Eubacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp. These changes were reversible within two weeks. Clostridium difficile toxin was not found.
Pharmacokinetics:
Suction
When oral moxifloxacin is absorbed rapidly and almost completely. The absolute bioavailability is about 91%. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin when taken in a dosage of 50 to 1200 mg once daily and 600 mg / day for 10 days is linear. The equilibrium state is achieved within 3 days. After a single application of 400 mg of moxifloxacin in the blood Cmax is reached within 0.5-4 hours and is 3.1 mg / l. After oral administration of moxifloxacin 400 mg 1 time per day and Sssmax Cssmin were 3.2 mg / L and 0.6 mg / l, respectively. When taken with food moxifloxacin noted a slight increase in the time to reach Cmax (at 2 hours) and Cmax slight reduction (approximately 16%), the duration of the suction are not changed. However, these data have no clinical significance and drug can be used regardless of the meal.
Distribution Moxifloxacin is rapidly distributed to tissues and organs and is associated with blood proteins (mainly albumin) by about 45%. The volume of distribution of about 2 L / kg. High concentrations of moxifloxacin in excess of those in the plasma generated in the pulmonary tissue (r. H. In epithelial fluid, alveolar macrophages) in the sinuses (maxillary and ethmoidal sinuses), nasal polyps, at inflammatory sites (contents bubbles at skin lesions). The interstitial fluid and in saliva moxifloxacin determined in a free, not bound to proteins form, at a concentration higher than in plasma. Furthermore, high concentrations of moxifloxacin determined in tissues of abdominal organs, peritoneal fluid and female genital organs.
Metabolism
Moxifloxacin biotransformation phase 2nd and excreted by the kidneys, and through the intestine as in unmodified form or in the form of inactive sulpho compounds (M1) and glucuronides (M2). Moxifloxacin is biotransformation microsomal cytochrome P450 system. Metabolites M1 and M2 are present in blood plasma in concentrations lower than the parent compound. According to the results of pre-clinical studies have shown that these metabolites have no negative effects on the body in terms of safety and tolerability. Excretion half-life of moxifloxacin is approximately 12 hours. Mean total clearance after the administration of 400 mg of 179-246 ml / min. Renal clearance of 24-53 ml / min. This indicates a partial tubular reabsorption of the drug. Balance masses of the parent compound and the metabolites 2nd phase is about 96-98%, which indicates the absence of oxidative metabolism. About 22% of a single dose (400 mg) excreted unchanged by the kidneys, about 26% – in the intestine.
Pharmacokinetics in different patient populations.
Age, gender and ethnicity.
In the study of the pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in both men and women have been identified in 33% of the differences in terms of AUC and Cmax. Absorption of moxifloxacin was not dependent on gender. Differences in AUC and Cmax were attributable to the difference in weight rather than gender, and are not considered clinically significant. It found no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in patients of different ethnic groups and different ages. Children.
The pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in children has not been studied.
Renal insufficiency.
No significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in patients with impaired renal function (including patients with creatinine clearance
Abnormal liver function.
There were no significant differences in the concentration of moxifloxacin in patients with impaired hepatic function (classes A and B according to Child-Pugh classification) compared with healthy volunteers and patients with normal liver function.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Safety of application of moxifloxacin during pregnancy has not been established and its use is contraindicated. Cases of reversible damage to the joints in children receiving some quinolones, however, no reports of the manifestation of this effect in the fetus (when the mother applied during pregnancy). In animal studies, reproductive toxicity was shown. The potential risk for humans is unknown. As with other quinolones, moxifloxacin causes damage to the cartilage of large joints in premature animals. Preclinical studies have shown that small amounts of moxifloxacin is released in breast milk. Data on its use in women during lactation are not available. Therefore, the appointment of moxifloxacin during breast feeding is contraindicated.
Conditions of supply of pharmacies
On prescription.
side effects
These adverse reactions reported with the use of moxifloxacin 400 mg (inward at sequential therapy [intravenous administration of the drug with its subsequent ingestion] and only i.v.), derived from clinical studies and post-marketing messages (in italics). Adverse reactions listed in the group “often” occurred at a frequency below 3%, except for nausea and diarrhea. In each frequency band adverse drug reactions are listed in descending order of significance. The frequency is determined as follows: often (1/10) infrequently (from
special instructions
In some cases, after the first use of the drug may develop hypersensitivity and allergic reactions, as should inform your doctor immediately. Very rarely, even after the first application of the preparation, anaphylactic reactions may progress to life-threatening anaphylactic shock. In these cases, treatment with Avelox should stop immediately and begin to carry out the necessary remedial measures (including anti-shock). In applying the drug Aveloks some patients may experience an elongation interval QT. Avelox drug should be used with caution in women and elderly patients. Since women than men have the QT interval is longer, they may be more sensitive to the drug, prolongs the QT interval. Elderly patients are also more exposed to drugs affecting the QT interval. QT prolongation is associated with an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias, including polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. QT interval elongation degree may increase with increasing concentration of the drug, however, do not exceed the recommended dose. Однако у пациентов с пневмонией корреляции между концентрацией моксифлоксацина в плазме крови и удлинением интервала QT отмечено не было. Ни у одного из 9000 пациентов, получавших Авелокс, не отмечалось сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и летальных случаев, связанных с удлинением интервала QT. При применении препарата Авелокс может увеличиваться риск развития желудочковых аритмий у пациентов с предрасполагающими к аритмиям состояниями. В связи с этим препарат Авелокс противопоказан при: изменениях электрофизиологических параметров сердца, выражающихся в удлинении интервала QT: врожденных или приобретенных документированных удлинениях интервала QT, электролитных нарушениях, особенно некоррегированной гипокалиемии; клинически значимой брадикардии; клинически значимой сердечной недостаточности со сниженной фракцией выброса левого желудочка; наличии в анамнезе нарушений ритма, сопровождавшихся клинической симптоматикой; применении с другими препаратами, удлиняющими интервал QT (см. раздел «Взаимодействие с другими лекарственными препаратами»). Препарат Авелокс следует применять с осторожностью: у пациентов с потенциально проаритмическими состояниями такими как острая ишемия миокарда и остановка сердца; у пациентов с циррозом печени (так как у данной категории пациентов нельзя исключить риск развития удлинения интервала QT).
При приеме препарата Авелокс сообщалось о случаях фульминантного гепатита, потенциально приводящего к развитию печеночной недостаточности (включая фатальные случаи) (см. раздел «Побочное действие»). Пациента следует информировать о том, что в случае появления симптомов печеночной недостаточности необходимо обратиться к врачу, прежде чем продолжить лечение препаратом Авелокс. При приеме препарата Авелокс сообщалось о случаях развития буллезных поражений кожи, таких как синдром Стивенса-Джонсона или токсический эпидермальный некролиз (см. раздел «Побочное действие»). Пациента следует информировать о том, что в случае появления симптомов поражения кожи или слизистых оболочек необходимо обратиться к врачу, прежде чем продолжить лечение препаратом Авелокс. Применение препаратов хинолонового ряда сопряжено с возможным риском развития судорог. Препарат Авелокс следует применять с осторожностью у пациентов с заболеваниями ЦНС и с нарушениями со стороны ЦНС, предрасполагающими к возникновению судорог или снижающими порог судорожной активности. Применение антибактериальных препаратов широкого спектра действия, включая препарат Авелокс, сопряжено с риском развития псевдомембранозного колита. Этот диагноз следует иметь в виду у пациентов, у которых на фоне лечения препаратом Авелокс развилась тяжелая диарея. В этом случае немедленно должна быть назначена соответствующая терапия. Препараты, угнетающие перистальтику кишечника, противопоказаны при развитии тяжелой диареи. Препарат Авелокс следует использовать с осторожностью у пациентов с миастенией gravis в связи с возможным обострением заболевания. На фоне терапии хинолонами, в том числе моксифлоксацином, возможно развитие тендинита и разрыва сухожилия особенно у пожилых и пациентов, получающих глюкокортикостероиды. Описаны случаи, которые возникли в течение нескольких месяцев после завершения лечения. При первых симптомах боли или воспаления в месте повреждения, прием препарата следует прекратить и разгрузить пораженную конечность. При применении хинолонов отмечаются реакции фоточувствительности. Однако при проведении доклинических и клинических исследований, а также при применении препарата Авелокс в практике не отмечалось реакций фоточувствительности. Тем не менее, пациенты, получающие препарат Авелокс, должны избегать воздействия прямых сол- нечных лучей и ультрафиолетового света. Применение препарата в форме таблеток для приема внутрь не рекомендуется у пациенток с осложненными воспалительными заболеваниями органов малого таза (например, связанными с тубоовариальными или тазовыми абсцессами). Не рекомендуется использовать моксифлоксацин для лечения инфекций, вызванных штаммами Staphylococcus aureus резистентными к метициллину (MRSA). В случае предполагаемых или подтвержденных инфекций, вызванных MRSA, следует назначить лечение соответствующими антибактериальными препаратами (см. раздел «Фармакодинамика»).
Способность препарата Авелокс подавлять рост микобактерий может стать причиной взаимодействия in vitro моксифлоксацина с тестом на Mycobacterium spp., приводящего к ложноотрицательным результатам при анализе образцов пациентов, которым в этот период проводится лечение препаратом Авелокс. У пациентов, которым проводилось лечение хинолонами, включая препарат Авелокс®, описаны случаи сенсорной или сенсомоторной полинейропатии, приводящей к парестезиям, гипестезиям, дизестезиям или слабости. Пациентов, которым проводится лечение препаратом Авелокс, следует предупредить о необходимости немедленного обращения к врачу перед продолжением лечения в случае возникновения симптомов нейропатии, включающих боль, жжение, покалывание, онемение или слабость (см. раздел «Побочное действие»). Реакции со стороны психики могут возникнуть даже после первого применения фторхинолонов, включая моксифлоксацин. В очень редких случаях депрессия или психотические реакции прогрессируют до возникновения суицидальных мыслей и поведения с тенденцией к самоповреждению, включая суицидальные попытки (см. раздел «Побочное действие»). В случае развития у пациентов таких реакций следует отменить препарат Авелокс и принять необходимые меры. Необходимо соблюдать осторожность при применении препарата Авелокс пациентами с психозами и/или с психиатрическими заболеваниями в анамнезе. Из-за широкого распространения и растущей заболеваемости инфекциями, вызванными резистентной к фторхинолонам Neisseria gonorrhoeae при лечении пациентов с воспалительными заболеваниями органов малого таза не следует проводить монотерапию моксифлоксацином, за исключением случаев, когда присутствие резистентной к фторхинолонам N. gonorrhoeae исключено. Если нет возможности исключить присутствие резистентной к фторхинолонам N. gonorrhoeae, необходимо решить вопрос о дополнении эмпирической терапии моксифлоксацином соответствующим антибиотиком, который активен в отношении N. gonorrhoeae (например, цефалоспорин). Дисгликемия
Как и в случае с другими фторхинолонами, при применении препарата Авелокс отмечалось изменение концентрации глюкозы в крови, включая гипо- и гипергликемию. На фоне терапии препаратом Авелокс дисгликемия возникала преимущественно у пожилых пациентов с сахарным диабетом, получающих сопутствующую терапию пероральными гипогликемическими препаратами (например, препаратами сульфонилмочевины) или инсулином. При проведении лечения у пациентов с сахарным диабетом рекомендуется тщательный мониторинг концентрации глюкозы в крови (см. раздел «Побочное действие»).
Влияние на способность управлять автомобилем и движущимися механизмами.
Фторхинолоны, включая моксифлоксацин, могут нарушать способность пациентов управлять автомобилем и заниматься другими потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенного внимания и быстроты психомоторных реакций, вследствие влияния на ЦНС и нарушения зрения.
Storage conditions
At temperatures above 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Dosing and Administration
Рекомендуемый режим дозирования моксифлоксацина: 400 мг (1 таблетка) 1 раз в день при инфекциях, указанных выше. Не следует превышать рекомендуемую дозу. Таблетки следует проглатывать целиком, не разжевывая, запивая достаточным количеством воды, вне зависимости от приема пищи.
Продолжительность лечения
Продолжительность лечения определяется локализацией и тяжестью инфекции, а также клиническим эффектом: Обострение хронического бронхита: 5-10 дней, Острый синусит: 7 дней, Неосложненные инфекции кожи и подкожных структур: 7 дней, Внебольничная пневмония: общая продолжительность ступенчатой терапии (внутривенное введение с последующим приемом внутрь) составляет 7-14 дней, Осложненные инфекции кожи и подкожных структур: общая продолжительность ступенчатой терапии моксифлоксацином (внутривенное введение с последующим приемом внутрь) составляет 7-21 день, Осложненные интраабдоминальные инфекции: общая длительность ступенчатой терапии (внутривенное введение с последующим приемом внутрь) составляет 5-14 дней, Неосложненные воспалительные заболевания органов малого таза – 14 дней. Не следует превышать рекомендуемую продолжительность лечения. По данным клинических исследований продолжительность лечения препаратом Авелокс в таблетках может достигать 21 день.
Elderly patients
Изменения режима дозирования у пожилых пациентов не требуется.
Children
Эффективность и безопасность применения моксифлоксацина у детей и подростков не установлена.
Нарушение функции печени
Пациентам с нарушениями функции печени, изменения режима дозирования не требуется (для применения у пациентов с циррозом печени см. раздел «Особые указания»).
Почечная недостаточность
У пациентов с нарушением функции почек (в том числе при тяжелой степени почечной недостаточности с клиренсом креатинина
Применение у пациентов различных этнических групп
Изменения режима дозирования не требуется.
Information
Appearance may differ from that depicted in the picture. There are contraindications. You need to read the manual or consult with a specialist
Additional information
| Weight | 0.100 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Bayer Pharmaceuticals |










There are no reviews yet.